What Is Chainlink (LINK)?
Chainlink (LINK) is a decentralized blockchain oracle network that enables smart contracts to communicate with real-world data and services outside of blockchain networks. Chainlink serves as a "bridge" between blockchains and off-chain environments, enabling smart contracts to connect securely and swiftly to data sources. Its purpose is to connect smart contracts on blockchains to actual data and events. It is a distributed system of nodes that offer information and data from off-blockchain sources to on-blockchain smart contracts through oracles.

Source and Copyright © Chain.link
This system employs blockchain technology to enable secure computation both on and off the chain, facilitating what it refers to as hybrid smart contracts. Enterprises utilizing Chainlink are able to access major blockchain networks, such as Ethereum and Solana. Chainlink comprises numerous decentralized oracle networks, each consisting of multiple blockchain oracles that retrieve and authenticate data. This enables smart contracts using Chainlink to obtain data from dozens to hundreds of oracle nodes and combine the outcomes rather than depending on a single oracle.
LINK is the native cryptocurrency for the Chainlink network, which is designed to pay node operators. Chainlink's reputation system awards vendors with the most LINK with larger contracts and deducts tokens for failure to provide accurate information. The developers describe LINK as "an ERC20 token with additional ERC223 functionality that allows smart contracts to receive and process tokens in a single transaction.
Who Are the Founders and Investors of Chainlink?
Chainlink was established in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis. They jointly published a white paper presenting the Chainlink protocol and network with Cornell University professor Ari Juels in the same year. Sergey Nazarov founded Chainlink Labs, which owns and operates the Chainlink decentralized oracle network. Steve Ellis co-founded Chainlink and currently serves as the firm's CTO.
Chainlink Labs is a private company that has secured more than £90 million in seed, A, B, and C venture financings. Being a private company, it is not obliged to reveal its investors or funding sources. However, some information is available from media and according to Tracxn, Chainlink has raised funding from 36 investors, including 2020 Ventures and 35 others.
What Is Chainlink Price Today?
The current price of Chainlink is $13.39 with a 24-hour trading volume of $273,987,550. Chainlink is a cryptocurrency that has experienced significant price fluctuations over time. Here are some of the most significant moments in its price history:
- September 2017: Chainlink launched, with the first exchange rate of LINK detected at $0.1718990.
- 2018: Chainlink's price fluctuated between $0.60 and $0.28.
- 2019: Chainlink's price increased from $1.52 to $4.50, closing at $1.77.
- 2020: Chainlink's price increased by 536.06% from $1.770655 to $11.26, making it the top-performing year for Chainlink.
- August 2020: Chainlink's price soared over the $20 mark for the first time following a string of partnerships announced, including one with Provide.
- December 2020 - May 2021: Chainlink's price rose more than sixfold and reached an all-time high of $52.88
In 2023 LINK token experienced a negative trend from August to September, falling from $9.30 to $5.96. LINK returned to growth thanks to massive activity from major wallets, which boosted the value of the coin to $9.20, and the announcement of close collaboration with SWIFT on mass adoption of the cryptocurrency spurred Chainlink to growth.
In October the price range for LINK token was between $5.00 and $10.00, and positive prognosis for it’s price is varry around 15$, therefore, any predictions about the price of LINK should be taken as estimates and not as guarantees due to high volatility of crypto market as whole.
What Is the All-time High for Chainlink (LINK)?
The all-time high for Chainlink (LINK) is $52.70, which was recorded on May 10, 2021
What Is the All-time Low for Chainlink (LINK)?
The all-time low for Chainlink (LINK) is $0.148183, which was recorded on November 29, 2017.
What Is the Market Cap of Chainlink (LINK)
Currently Chainlink market cap is $8,543,513,270 with total supply $1,000,000,000. It has fluctuated over time, with highs and lows depending on market trends, investor sentiment and partnerships. Current market cap is significantly lower than its market capitalization high of $9 billion, which was recorded on 10 May 2021.
How and Where to Buy Chainlink
Chainlink is a cryptocurrency that can be bought on various exchanges. Here are the steps to buy Chainlink on some popular exchanges, such as Binance, Kraken, Coinbase or Gate.io. To buy any crypto on a centralised crypto exchange, you'll need to create an account and complete verification steps.
If you do not want to trade, but just want to add money to your purse, it is easier to make transactions through an exchanger, choosing the best rate and checking the reliability.
How to Sell Chainlink (LINK)?
The process of selling Chainlink is similar to its buying, but after performing KYC, you will need to create “Sell” order.
Is Chainlink Coin Legit?
Chainlink possesses a stable presence, growing popularity, and reliability, having secured billions of dollars in DApps. It is also rated as the 23rd most valuable cryptocurrency with a market dominance of around 0.38%. The developers behind Chainlink have recently unveiled their plans to upgrade the present version to a more progressive version - Chainlink 2.0.
Furthermore, Chainlink facilitates digital agreements to make informed decisions based on real-world data, elevating online deals to be more intelligent and reliable for all. There have been concerns raised regarding the legitimacy of Chainlink. Some have claimed it to be a scam or a less valuable asset. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive research and due diligence prior to investing in Chainlink or any other cryptocurrency.
What Makes Chainlink Unique?
Chainlink aims to connect blockchain smart contracts with the real world. It does this by functioning as a decentralized oracle network that supplies real-time data to smart contracts on the blockchain. It greatly improves their abilities by enabling access to data outside the blockchain and off-chain computing, while maintaining the security and reliability assurances of blockchain technology.
It functions similarly to an API for blockchains, enabling different blockchain applications to communicate with each other. It functions similarly to an API for blockchains, enabling different blockchain applications to communicate with each other. Chainlink enables smart contracts to interact with the world while preserving the security, transparency, and trust principles of blockchain technology. The network is highly decentralized and secure, and it gathers information on market pricing from various top sources to create an aggregated value.
What is Chainlink Oracles?
Oracles are entities that connect blockchains to external systems, thereby enabling smart contracts to execute based on inputs and outputs originating from the blockchain. They provide external data that triggers smart contract execution when specified conditions are met.
If users require offline data access, they may request a contract from the relevant oracles. Contracts come in three types.
- Reputation Contract: verifies the legitimacy and performance history of an oracle provider before evaluating and discarding unreliable nodes. It checks the past records of oracles and evaluates their performance to ensure that the data provided is trustworthy and reliable.
- Order-Matching Contract: requests Chainlink nodes, collects their bids, and fulfills the request by selecting the appropriate number and type of nodes. It communicates the request of the Requesting Contract to Chainlink nodes and solicits their bids. Then, it selects the appropriate number and type of nodes to fulfill the request.
- Aggregating Contract: checks all of the data from the selected oracles to obtain and verify the results. It takes the data points, assesses the validity of each one, and returns a weighted score to the user, using the sum of all the received data. It collects data from various sources, verifies, and reconciles it to provide an accurate result.
How to Mine Chainlink
Chainlink cannot be mined like Bitcoin or other coins that utilize the Proof of Work algorithm. Chainlink is developed on the Ethereum platform and produces an ERC-20 token called LINK, which means it cannot be mined. Instead, it involves Proof of Stake, where people can stake LINK, providing a current return on investment (ROI) of around 4.75%. Staking is similar to mining, where validators (who are developers) verify Chainlink transactions and receive additional LINK as a reward.
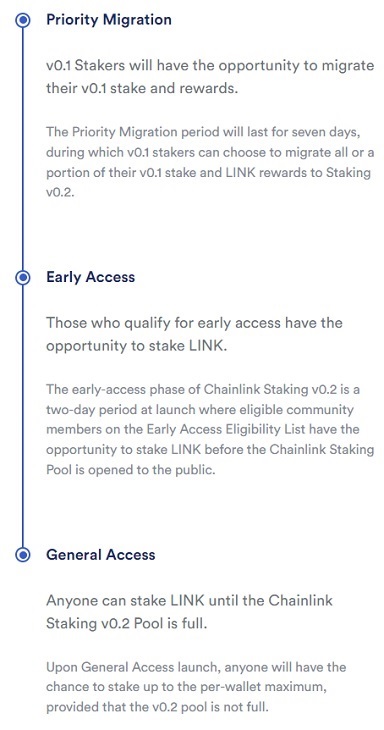
Chainlink Staking v0.2 timeline. Source and Copyright © Chain.link
How to Keep Your LINK Tokens Safe?
Since LINK is an ERC20 token that deploys on-chain contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, you'll need to look for a wallet that supports these tokens. Choose a reputable wallet such as MyEtherWallet (MEW) or MyCrypto. Alternatively, if you are holding a significant amount of money in crypto assets, it is preferable to use a reputable hardware wallet like a Ledger Nano S/X. A hardware wallet is not connected to the internet and is invulnerable to most common attacks. This is the safest way to store your LINK tokens.
Pros and Cons of Chainlink
| Pros | Cons |
| Chainlink is a framework for building Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs) that connect smart contracts to other blockchains, off-chain data and more | Chainlink is a relatively new technology and is still in development, which means there may be some risks associated with using it |
| Chainlink enables non-blockchain enterprises to securely connect with blockchain platforms | Chainlink's LINK token is built on the Ethereum platform, which means it is subject to the same risks as Ethereum |
| Chainlink uses blockchain technology to securely enable computations on and off chain, supporting what it calls hybrid smart contracts | Chainlink's success is dependent on the adoption of blockchain technology, which is still in its early stages. |
| Chainlink can facilitate secure communications between Ethereum projects and various off-chain data. | Chainlink's success is dependent on the adoption of blockchain technology, which is still in its early stages. |
| Chainlink's decentralized oracle can connect many types of data with various blockchains, creating many potential applications for Chainlink. | Chainlink's success is dependent on the adoption of blockchain technology, which is still in its early stages. |
Summary
The ICO boom has brought numerous new projects to the cryptocurrency market. It has survived the crypto winter and has become a foundational infrastructure for the smart contract economy. Chainlink's goal is to provide off-chain data to cryptocurrency blockchains, and it utilizes a network of oracles to deliver this data. With over 1,000 projects and a maximum token supply of 1 billion, Chainlink has established itself as a dependable and efficient project in the cryptocurrency market.
The closer the bull run in crypto, the more attractive scaling solutions like Chainlink appear to be as investments. Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that enhances the capabilities of global blockchains and offers secure access to off-chain data. It is a unique project that does not seek to compete against other cryptocurrencies but instead aims to advance the entire sector through its unique protocols.