What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum (ETH) is the second most popular cryptocurrency and second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization after BTC, but unlike its counterpart, Ethereum aims to be more than just a simple medium of exchange or store of value. Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that features smart contract functionality.
Source and Copyright © Ethereum.org
Developers can use Ethereum to run decentralized applications (dApps) that are driven by smart contracts, which facilitate the automatic execution of agreements without requiring a trusted third party, and issue new crypto assets, known as Ethereum tokens, Ethereum's native cryptocurrency or Ether (ETH), which is used to build and secure the network. It is an inflationary token that adheres to the ERC-20 token standard.
Ethereum uses smart contracts and is maintained by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). EVM compiles and deploys smart contracts on the decentralized network.
Who Are the Founders and Investors of Ethereum?
Ethereum was founded by a group of eight individuals who played crucial roles in the early development of the platform. The list of Ethereum's co-founders includes Vitalik Buterin, Mihai Alisie, Anthony Di Iorio, Amir Chetrit, Charles Hoskinson, Gavin Wood, Jeffrey Wilcke, and Joseph Lubin.
Ethereum was conceived in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, the most well-known of the co-founders and still active in the work of the project, development work began in 2014, which was crowdfunded, and the network went live on 30 July 2015. Another key person who played a crucial role in the development of Ethereum is Gavin Wood, a co-founder who implemented Ethereum in C++ programming language and was the first to run the Ethereum test net. Wood published the Ethereum Yellow Paper in April 2014 and later developed Ethereum's native programming language, Solidity.
Ethereum has received funding from various investors over the years. Here are several of them:
- Winklevoss Capital
- #Hashed
- 8 Decimal Capital
- Visary Capital
- Outlier Ventures
- Pipeline Capital
- Inflection VC
- Maven 11 Capital
- etc.
In addition to these venture capital firms, there are also individual investors who have invested in Ethereum, including Joseph Lubin, Richard Sherman, and Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss. Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum, is also considered an investor in the platform.
Ethereum's development was funded by an online public crowd sale from July to August 2014, in which participants bought the Ethereum value token (ETH) with another digital currency, Bitcoin.
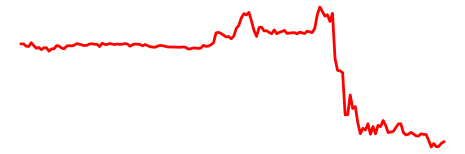
What Is Ethereum Price Today?
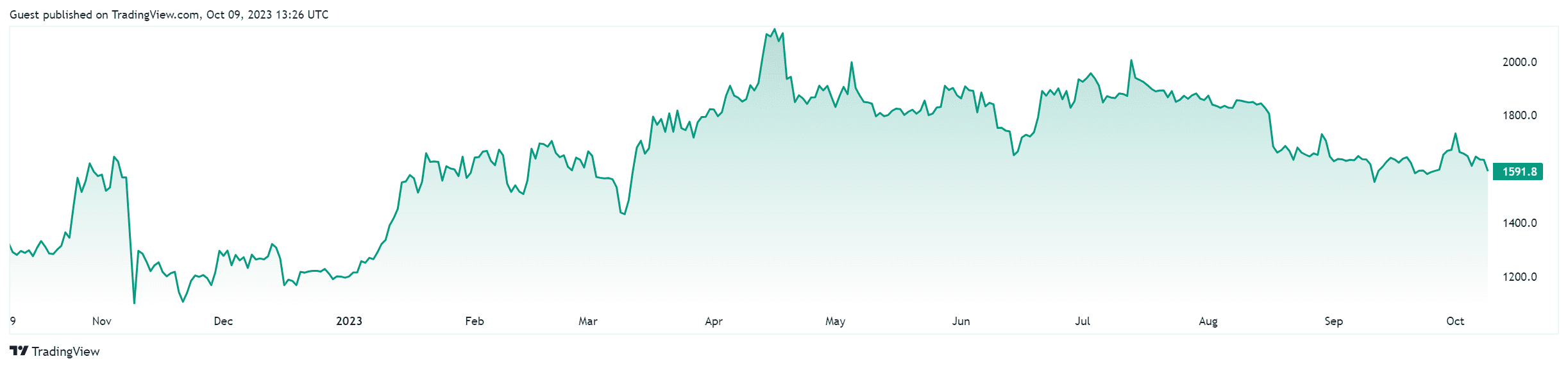
Source and Copyright © TradingView
The current price of Ethereum (ETH) is $2,533.09 with a trading volume of $27,287,623,180. The current circulating supply is 120,724,829 ETH. Trading volume for 24 hours and price changes for the same time can be found here.
What Is the All-time High for Ethereum?
Ethereum all-time high was $4,891.70 on October 8, 2021. Ethereum's price has been on the rise in 2021, and there are several factors that could have contributed to the all-time high: the growing popularity of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications built on the Ethereum blockchain, the increasing demand for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that are also built on the Ethereum blockchain, the launch of Ethereum 2.0, which is a major upgrade to the Ethereum network, and the increasing institutional interest in Ethereum.
What Is the All-time Low for Ethereum?
Ethereum all-time low was $0.432979, which happened on October 20, 2015. The year 2015 was the only time when Ethereum was worth one dollar or less, with the exception of January 2016, with $0.93. There weren't many significant events for the Ethereum price history in 2015 to cause this all-time low.
What Is the Market Cap of Ethereum?
The market cap for Ethereum is $328,310,634,785. It's important to note that the market cap of Ethereum can fluctuate rapidly, and it is important to stay informed and keep an eye on market trends to make informed decisions when investing in cryptocurrencies.
How and Where to Buy Ethereum?
Here are some popular platforms and exchanges where you can buy Ethereum:
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to buy Ethereum:
- Choose a cryptocurrency exchange or platform that supports Ethereum, such as Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken.
- Create an account on the exchange or platform and complete the verification process.
- Fund your account using a bank transfer, credit card, or other payment method supported by the exchange or platform.
- Once your account is funded, navigate to the Ethereum trading page and select the amount of Ethereum you want to buy.
- Review the transaction details and confirm the purchase.
- Your Ethereum will be deposited into your exchange or platform wallet.
It's important to note that the process of buying Ethereum may vary slightly depending on the exchange or platform you choose.
How to Sell Ethereum?
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to sell Ethereum:
- Choose a cryptocurrency exchange or platform that supports Ethereum, such as Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken.
- Create an account on the exchange or platform and complete the verification process.
- Transfer your Ethereum to the exchange or platform wallet if it's not already there.
- Navigate to the Ethereum trading page and select the amount of Ethereum you want to sell.
- Review the transaction details and confirm the sale.
- Withdraw your funds to your bank account or other payment method supported by the exchange or platform.
It's important to note that the process of selling Ethereum may vary slightly depending on the exchange or platform you choose.
Is Ethereum Legit?
Yes, Ethereum is a legitimate cryptocurrency and blockchain platform. Ethereum has been around since 2015 and has a large and active community of developers, users, and investors. However, as with any cryptocurrency, there are risks associated with investing in Ethereum, including the potential for scams and fraud.
Be careful and be sure to study the laws of your country before any transactions with Ethereum, because in some countries it may be illegal.

What Makes Ethereum Unique?
Ethereum's unique features and applications make it a versatile and secure platform for creating, connecting, and monetizing a growing ecosystem of Dapps and smart contracts. Here are some of the key features that make Ethereum unique:
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing smart contracts facilitated by Ethereum eliminate the necessity of a central authority in transactions.
- Decentralized Applications (Dapps): Ethereum allows developers to create and implement decentralized applications, where decision-making authority lies with the participants.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): Ethereum has its own virtual machine, which allows developers to write and execute smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Ether: Ether is Ethereum's cryptocurrency used to pay transaction fees or "gas" and can also be used as a store of value.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Ethereum allows you to create DAOs for democratic decision-making.
- Flexibility: Ethereum is a flexible platform for building decentralized apps with Solidity and the Ethereum Virtual Machine. Developers benefit from a rich ecosystem and best practices.
How to Mine Ethereum?
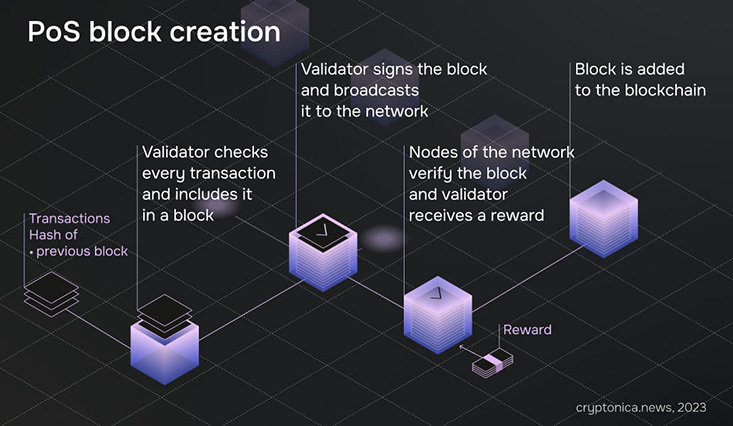
Mining Ethereum using proof-of-stake (PoS) is a more energy-efficient and secure way to validate transactions and mint new ETH based on the validator's ether holdings. Here are the steps to mine Ethereum using PoS:
- Staking: Validators must stake a minimum of 32 ETH to participate in the validation process and earn staking rewards.
- Choosing the right software: Validators must choose a client software that supports Ethereum PoS, such as Prysm, Lighthouse, or Teku.
- Joining a mining pool: Validators can join a mining pool to increase their chances of being selected as a block proposer and earn more rewards. Some popular mining pools for Ethereum PoS are Rocket Pool, Lido, and Stkr.
- Running the client software: Validators must run the client software on their computer or server to participate in the validation process and earn rewards.
- Validating transactions: Validators validate transactions and create new blocks by proposing them to the network. Validators are selected randomly based on their staked ETH and the length of time they have been staking.
- Earning staking rewards: Validators earn staking rewards for validating transactions and creating new blocks. The rewards are paid out in ETH and are proportional to the amount of ETH staked.
Mining Ethereum using PoS requires less computational power and energy consumption compared to proof-of-work (PoW) mining. Validators can earn rewards by participating in the validation process and contributing to the security of the Ethereum network.
How to Keep Your Ethereum Safe?
Here are some tips on how to keep your Ethereum safe:
- Use a reputable wallet: Choose a reputable wallet that is known for its security features. Some popular Ethereum wallets include MyEtherWallet, Exodus, and Ledger Nano S.
- Keep your private key safe: Your private key is the key to your Ethereum wallet, and it should be kept safe and secure. Write it down and keep it in a safe place, or use a hardware wallet to store your private key offline.
- Bookmark your wallet: If you use a web wallet, bookmark the site to protect yourself against phishing scams.
- Triple-check everything: Transactions can't be reversed, and wallets can't be easily recovered, so take precautions and always be careful. Always triple-check the address you're sending Ethereum to, and make sure you're sending it to the right address.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all your Ethereum wallets to add an extra layer of security.
- Choose strong passwords: Choose strong and unique passwords for your Ethereum wallets. Avoid using common passwords or easily guessable phrases. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords.
- Regularly back up your wallet: Regularly back up your wallet and store the backup in a safe and secure location. This ensures that you can recover your Ethereum holdings in the event of a lost, stolen, or damaged wallet.
Pros and Cons of Ethereum
Here are the pros and сons of Ethereum:
| Pros of ETH | Cons of ETH |
| Decentralized design that effectively distributes knowledge and trust among network members, removing the need for a central body to run the system and mediate transactions | Scalability issues; the blockchain network work nicely during calm periods, but whenever a bull market kicks in and millions of new investors join crypto, Ethereum simply can’t keep up |
| Smart contracts; these computer protocols intend to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract | Volatility, because the price of Ether is very volatile, which can result in significant gains as well as significant losses |
| Fast and reliable transaction processing, with confirmations taking only a short time, from 15 seconds to five minutes | Competition, because Ethereum now competes against other currencies like Litecoin (LTC), Ripple (XRP), etc. |
| Investment opportunities, because one can also invest in firms that are developing apps that use the Ethereum network | Risk, because investing in Ethereum comes with its fair share of risks, and there's no guarantee that it will succeed long-term |
| Uncensorable information, because Ethereum is decentralized and isn’t limited by a regulatory body, the information stored on the blockchain can remain alive and uncensorable | High fees, which can be inconvenient, and the network can get bogged down at times due to a high volume of transactions, causing slower transaction times and higher fees |
| First-mover advantage, because Ethereum is the world’s first blockchain network that supports smart contracts, giving it a first-mover advantage in the crypto market | |
| Use cases; Ethereum has many use cases and provides the foundation for several different technologies |
Why Is the Ethereum Transition from PoW to PoS Important?
The Ethereum blockchain is undergoing a significant technical update, transitioning from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, also known as Ethereum 2.0 or Eth2.
The transition began with the Beacon Chain, which enabled users to stake their Ether (ETH) and become validators. However, Phase 0 did not affect the main Ethereum blockchain, and both the Beacon chain and mainnet will eventually be linked with the Merge.
The transition from PoW to PoS is an important development for Ethereum, and here's why:
- PoS is more secure, less energy-intensive, and better for implementing new scaling solutions compared to the previous PoW architecture.
- PoS is more accessible, as anyone can participate if they have the funds rather than requiring expensive hardware.
- PoS is faster, more scalable, and can process more transactions per second than PoW.
- PoS requires less power than mining on a PoW network, making it more environmentally friendly.
The transition to PoS will enable Ethereum to introduce new features and capabilities, such as sharding, which will divide the network into shard chains that share the load of Ethereum, theoretically reducing network congestion and increasing transaction throughput.
Summary
Ethereum is a blockchain-based platform that is most commonly known for its native cryptocurrency, ether (ETH). It is a decentralized global software platform powered by blockchain technology that natively supports smart contracts, an essential tool behind decentralized applications. Ethereum allows users to make transactions, earn interest on their holdings through staking, and interact with the network.
Ethereum's transition to the proof-of-stake protocol, which enables users to validate transactions and mint new ETH based on their ether holdings, is part of a significant upgrade to the Ethereum platform.
Ethereum has many features, including decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and it is used as a way to interact with the network rather than as a way to transfer money, though it can do that too. However, Ethereum has some disadvantages, such as volatility, high fees, scalability issues, and competition.
One should DYOR and weigh its risk tolerance before investing in Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies. It is important to choose a legit and reliable exchange to make trading and investing in ETH secure.