
What is Staking in Crypto and How to Use it to Make Money?
Uncover the secrets of crypto staking in this detailed guide. Discover how digital assets can be pu to work to generate passive income, much like a high-yield savings account.Unravel the mechanics, rewards, and potential risks of staking in the cryptocurrency universe.
In this article, we're going to explore a concept that's integral to many blockchain networks. Staking. It's a term that's often heard around in the crypto community, but what does it really mean? How does it work, and why is it so important?
Staking is a key aspect of many cryptocurrencies, therefore by understanding it, you can better understand how these digital economies function. It's a bit like earning interest in a traditional bank account but with a twist. Instead of simply depositing your money and waiting for the interest to accumulate, staking involves actively participating in the network's operations.
Staking has turned into an effective tool for users looking to maximize their digital assets' return. It's a concept that's deeply rooted in the principles of decentralization and participation, principles that are at the very heart of blockchain technology.
In the following sections, we'll break down the concept of staking in a way that's easy to understand, even if you're new to the world of crypto. We'll explore its origins, how it works, its benefits, and potential risks.
What is Crypto Staking?
Staking refers to the process of participating in the validation of transactions on a blockchain network. It involves holding a certain amount of a particular cryptocurrency in a digital wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. This includes activities like transaction validation, security, and governance.
Staking is a key component of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and its variant consensus mechanisms, which are alternatives to the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism that Bitcoin and many other early cryptocurrencies use.
Here's a simple analogy: think of staking as putting down a deposit to secure a spot in a club. The more you're willing to deposit (or stake), the more likely you are to be chosen as a member (or in this case, a validator). Once you're a member, you can participate in the club's activities and earn rewards.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, these rewards come in the form of additional coins. The more coins you stake, the higher your potential rewards. It's a way of incentivizing participation in the network and ensuring its smooth operation.
But staking isn't just about earning rewards. It's also about securing the network. By staking coins, validators have a vested interest in maintaining the network's integrity. If they attempt to cheat the system, they risk losing their staked coins, making staking a self-regulating mechanism.
In essence, crypto staking allows users to earn passive income from their staked coins, while also contributing to the security, efficiency, and decentralization of the blockchain network.

What is Proof of Stake Consensus?
To fully understand the concept of staking, first, you need to understand the underlying mechanism that makes it possible: the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. This algorithm is the backbone of many cryptocurrencies and is what sets them apart from the original cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, which uses a different consensus system called Proof of Work (PoW).
In a PoW system, miners compete against each other to solve complex mathematical problems, a process that requires significant computational power and energy. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with some cryptocurrency.
In contrast, the PoS system eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining. Instead of miners, we have validators. These validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to stake as collateral. The more coins a validator stakes, the higher their chance of being chosen to create a new block.
Once a validator is chosen, they validate the transactions within the block, sign off on it, and add it to the blockchain. They are then rewarded with transaction fees and sometimes additional coins. This reward serves as an incentive for validators to act honestly. If they validate fraudulent transactions, they lose their stake and their rights as a validator.
The PoS consensus algorithm is a key component of the staking process. It not only provides a more sustainable and scalable solution to blockchain validation but also opens up opportunities for coin holders to participate in the network and earn rewards, thereby promoting greater decentralization and security.
In essence, Proof of Stake transforms the process of blockchain validation from a competitive race into a collaborative effort, where the focus shifts from computational power to the amount of stake and willingness to contribute to the network's security and efficiency.
How Does Staking Work?
Now that we've established what crypto staking is, let's delve into the mechanics of how it works. While the specifics can vary depending on the blockchain, the general principles remain the same.
Choosing a Coin and Wallet
The first step in staking is choosing a cryptocurrency that uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or a variant consensus mechanism. Some popular staking coins include Ethereum (which is transitioning to PoS), Cardano, and Polkadot. Once you've chosen a coin, you'll need a compatible wallet where you can store your coins. This could be a web wallet, a mobile wallet, or a hardware wallet, depending on what's supported.
Acquiring and Staking Coins
The next step is to acquire the coins you wish to stake. This can be done through a crypto exchange or other means. Once you have the coins, you can stake them directly from your wallet. The process usually involves clicking a 'stake' button and choosing the amount you wish to stake.
Becoming a Validator or Delegator
In PoS systems, stakers can either become validators or delegators. Validators are responsible for creating new blocks and validating transactions. They need to run a node, which requires technical knowledge and resources. Delegators, on the other hand, can 'delegate' their coins to a validator. The validator stakes these coins on their behalf and shares the rewards. This allows less technical users to participate in staking.
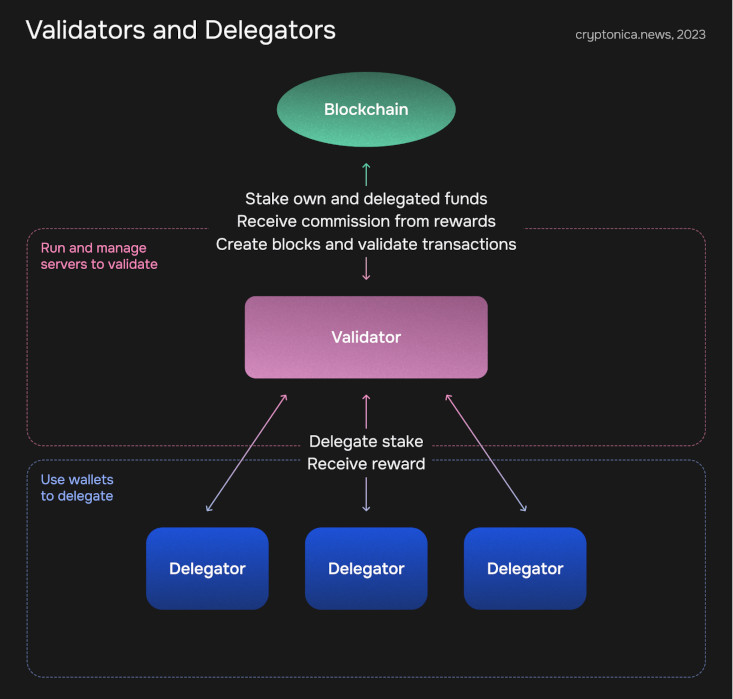
Earning Rewards
Once you've staked your coins, you can start earning rewards. These rewards are usually distributed automatically to your wallet. The frequency and amount of rewards can vary depending on the blockchain. Some networks offer fixed rewards, while others adjust the rewards based on the total amount of staked coins.
Unstaking and Selling
If you decide to stop staking, you can 'unstake' your coins. However, keep in mind that some networks have an 'unbonding' period during which your coins are locked. Once this period is over, you can sell your coins on a crypto exchange.
Some crypto exchanges even offer staking programs, handling the technical burden for a portion of the rewards. However, it's worth noting that exchange-based staking programs have recently come under regulatory scrutiny. Allegations of breaching securities laws have been leveled against several providers, including the well-known Coinbase. This underscores the importance of understanding the intricacies of staking and the potential risks involved.
Is Crypto Staking a Profitable Venture?
One of the most enticing aspects of crypto staking is the potential to earn passive income. But how much can you actually earn through staking? The answer to this question isn't straightforward, as it depends on several factors:
The cryptocurrency you're staking: Different cryptocurrencies offer different staking rewards. These rewards can be influenced by factors such as the total supply of the cryptocurrency, the inflation rate, and the total amount of coins being staked by others.
The staked amount: Generally, the more coins you stake, the higher your potential rewards. This is because, in a PoS system, the chance of being chosen as a validator is proportional to the number of coins you have staked.
The network's staking model: Some networks have a fixed reward rate for staking, while others adjust the rate based on the total amount of coins being staked. In the latter case, if more users start staking, the reward rate may decrease.
The period of staking: Some networks offer higher rewards to those who are willing to lock up their coins for a longer period. This is known as a lock-up period, and it can range from a few days to a few years.
The level of involvement: If you're running a validator node, you might earn more rewards than if you're delegating your stake to someone else, as delegators often have to share a portion of their rewards with the validator.
Given these variables, it's difficult to provide a definitive figure for potential staking earnings. However, annual returns can range from as low as 1-2% to as high as 10-15%, or even more in some cases. It's important to do your own research and understand the staking model of the specific cryptocurrency you're interested in.
Benefits of Staking Crypto
Staking crypto offers a multitude of benefits, making it an attractive option for many cryptocurrency enthusiasts. Here are some of the key advantages:
One of the most appealing aspects of staking is the opportunity to earn passive income. By simply holding and staking your coins, you can earn rewards in the form of additional coins. This can be a steady source of income, much like earning interest on a savings account.
Staking contributes to the security of the blockchain network. Validators have a vested interest in maintaining the network's integrity, as any dishonest behavior could lead to their staked coins being forfeited. This makes the network more secure and trustworthy.
Some blockchain networks allow stakers to participate in network governance. This means that stakers can have a say in the future development of the network, including decisions about upgrades and changes to the protocol.
Staking is a key component of the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism, which is much more energy-efficient than the traditional Proof of Work mechanism used by Bitcoin and other early cryptocurrencies. This makes staking a more sustainable option for maintaining and securing a blockchain network.
Unlike mining, which requires significant computational power and energy resources, staking has a much lower entry barrier. Anyone with some coins and a compatible wallet can participate in staking, making it more accessible to the average user.
In addition to earning staking rewards, there's also the potential for the staked coins to appreciate in value. If the price of the cryptocurrency increases, stakers could realize significant gains on their staked coins.

Risks of Staking
Staking cryptocurrencies offers numerous benefits, however, it has the other side of the coin. You should be aware of the potential risks before you decide to stake your digital assets. Here are some of the key risks:
Price Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility. The value of your staked coins can fluctuate, sometimes dramatically, which could impact the value of your staking rewards and your initial stake. If the price of the cryptocurrency falls significantly, you could end up with less value than you initially staked.
Slashing
In some Proof of Stake networks, validators who act maliciously or fail to stay online and perform their duties can be penalized through a process called slashing. This means a portion of their staked coins could be taken away. If you're running your own validator node, you need to ensure it's reliable and secure to avoid potential slashing.
Lock-Up Periods
When you stake your coins, they are often locked up for a certain period of time. During this period, you can't sell or move your coins, which could be a disadvantage if you need liquidity. Additionally, if the market drops during your lock-up period, you won't be able to sell off your assets to mitigate losses.
Network Risks
Staking also carries risks associated with the specific blockchain network. These could include security vulnerabilities, software bugs, or major changes to the network's protocol. Any of these issues could potentially impact the value of your staked coins and rewards.
Regulatory Risks
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Changes in regulations or legal status could impact the staking process and the value of your staked coins.
Delegation Risks
If you're delegating your stake to a validator, you're relying on their honesty and competence. If they behave dishonestly or fail to perform their duties correctly, your stake and rewards could be at risk.
You can mitigate these risks, by doing your due diligence and staking wisely. As always, never stake more than you can afford to lose, and consider diversifying your investments to spread your risk.
FAQ
What cryptocurrencies can you stake?
You can stake any cryptocurrency that operates on a Proof of Stake (PoS) or a variant consensus mechanism. Some of the most popular cryptocurrencies for staking include Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, Polkadot, Tezos, and Algorand. However, the list is continually growing as more cryptocurrencies adopt PoS mechanisms.
How are staking rewards calculated?
Staking rewards are calculated based on several factors, including the amount of cryptocurrency you're staking, the total amount of cryptocurrency staked on the network, the inflation rate of the cryptocurrency, and the specific staking model of the blockchain.
How profitable is staking?
The profitability of staking depends on various factors, including the staking rewards of the specific cryptocurrency, the price of the cryptocurrency, the length of time you're willing to stake, and market conditions.
Is crypto staking worth it?
Whether crypto staking is worth it or not depends on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance. Staking can provide a steady stream of passive income and allows you to participate in the network's governance. However, it also comes with risks, including price volatility and potential loss of your staked coins.

























