
Bitcoin Halving Event 2024. What's Next?
Understanding Bitcoin halving. Discover its history, the economic theories behind it, and its potential impact on future prices in our comprehensive guide.
While the supply of traditional fiat currencies constantly changes under the guidance of national central banks, Bitcoin operates differently. Although Bitcoin exists in the digital sphere, its production isn't limitless. Its intrinsic value lies in its verifiable scarcity.
Two fundamental principles underscore Bitcoin's scarcity. Firstly, there's a hard cap of 21 million bitcoins. The second principle is the halving. Every four years, the rate at which new bitcoins are introduced to the system is cut in half.
This halving event is important in managing the supply of new Bitcoins. It's a reason many view Bitcoin more as a store of value, similar to gold, than just another fiat currency.
But why does this matter? Why do enthusiasts and investors mark their calendars years in advance, eagerly awaiting this event? The halving isn't just a technical adjustment, it's a monumental moment that has historically shaken markets and ignited debates.
In this article, we'll delve into the Bitcoin halving, its history, and its potential implications for the cryptocurrency market.
What is the Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin's halving introduces a level of predictability and transparency into its monetary policy. With the halving set at predefined intervals, investors and users have clarity on Bitcoin's supply rate well into the future.
This mechanism serves as a foundational measure to ensure predictable supply and reinforce Bitcoin's intrinsic value through scarcity. Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin's pseudonymous founder, integrated the halving feature to regulate Bitcoin's issuance, drawing inspiration from the limited and deflationary attributes of commodities like gold.
To understand the significance of the Bitcoin halving, it is important to understand the fundamentals of how the Bitcoin network operates.
The Bitcoin network employs a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Within this system, miners equipped with specialized hardware engage in solving complex cryptographic puzzles in order to validate and confirm transactions. When they successfully solve such a problem, they get the right to add a new "block" of transactions to the blockchain. For this effort, they are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins – this process is known as the "block reward". It's this very block reward that undergoes a halving approximately every four years.
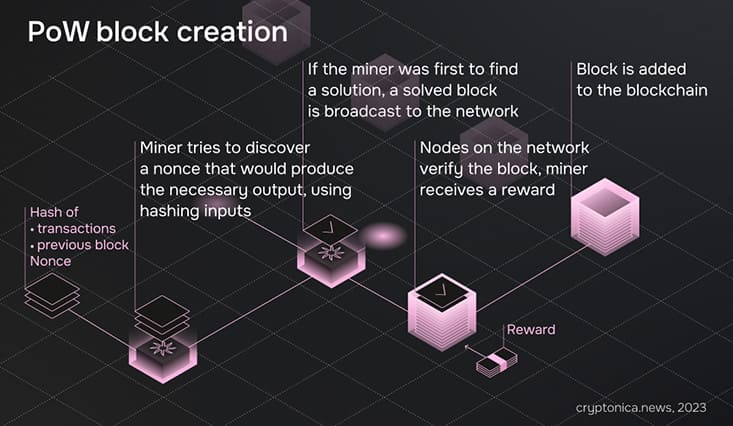
In 2009, when Bitcoin was first launched, the block reward was set at 50 Bitcoins. This means every time a miner added a block to the blockchain, they received 50 new Bitcoins. However, Bitcoin's design dictates that this reward would be halved every 210,000 blocks, which takes roughly four years to occur, given the 10-minute block time. As a result, in 2012, the block reward was reduced to 25 Bitcoins, in 2016 to 12.5, in 2020 to 6.25, and so on.
| Halving No | Date of Halving | Starting Block Reward | Post-Halving Block Reward |
| 1 | November 28, 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC |
| 2 | July 9, 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC |
| 3 | May 11, 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC |
| 4 (expected) | 2024 | 6.25 BTC | 3.125 BTC (expected) |
The halving will continue every four years until around the year 2140 when the block reward will decrease to less than a satoshi (the smallest unit of a bitcoin, 0.00000001 BTC). At this point, all 21 million bitcoins will have been mined, and miners will solely rely on transaction fees for revenue.
Why Bitcoin Halving is Important?
The fuss around the Bitcoin halving stems from its potential economic implications, historical price patterns following previous halvings, its direct impact on miners, and the broader attention it brings to the crypto space. Even though the event is programmed and predictable, its secondary effects on market behavior, miner dynamics, and public perception remain captivating topics of discussion and observation.
Here's why the halving is considered so crucial and why it attracts such interest:
Economic Model
As already mentioned, Bitcoin is often likened to gold in the context of being "digital gold". One of the reasons is its predictable supply curve and the enforced scarcity. There will only ever be 21 million bitcoins. The halving ensures that Bitcoin's issuance slows down over time, emphasizing this scarcity.
Each halving reduces Bitcoin's inflation rate. This means that fewer new bitcoins are entering circulation relative to the existing supply. By reducing the rate at which new bitcoins enter the market, halving events aims to reduce the inflationary pressures associated with a rapidly increasing money supply.
Historical Price Patterns
Historically, halving events have been followed by significant increases in the price of Bitcoin. This doesn't mean the price surges immediately post-halving, but in the months following past halvings, notable bull markets have occurred.
Given the historical patterns, many investors and traders anticipate potential price increases around halving events. This speculation can lead to increased buying, further driving up the price, at least in the short term.
Miner Revenue
The halving directly impacts miners' revenues since they receive fewer bitcoins for the same amount of work. If the value of Bitcoin doesn't increase to compensate for this reduced block reward, some miners might find it unprofitable to continue operations.
As the block reward decreases, miners need to rely more on transaction fees to cover their operational costs. This can impact decisions about which transactions to include in a block and may influence transaction fee costs.
If many miners were to stop their operations, it could reduce the overall security of the Bitcoin network. However, the Bitcoin difficulty adjustment mechanism (which adjusts approximately every two weeks) ensures that even with fewer miners, blocks are still produced roughly every 10 minutes.
Will the 2024 Bitcoin Halving Affect its Price?
Predicting exact price movements, especially for an asset as volatile as Bitcoin, is very difficult. As we approach the 2024 halving event, the crypto community is abuzz with theories and predictions. While we can analyze potential factors and historical precedents, it's important to remember that these are just indicators and not certainties.
If history is any indication, each previous halving has been followed by a substantial increase in Bitcoin's price. For instance, the year following both the 2016 and 2020 halvings saw significant bull runs. However, while historical patterns provide context, they don't guarantee future outcomes. Each cycle operates within unique global economic conditions and varying levels of cryptocurrency adoption.
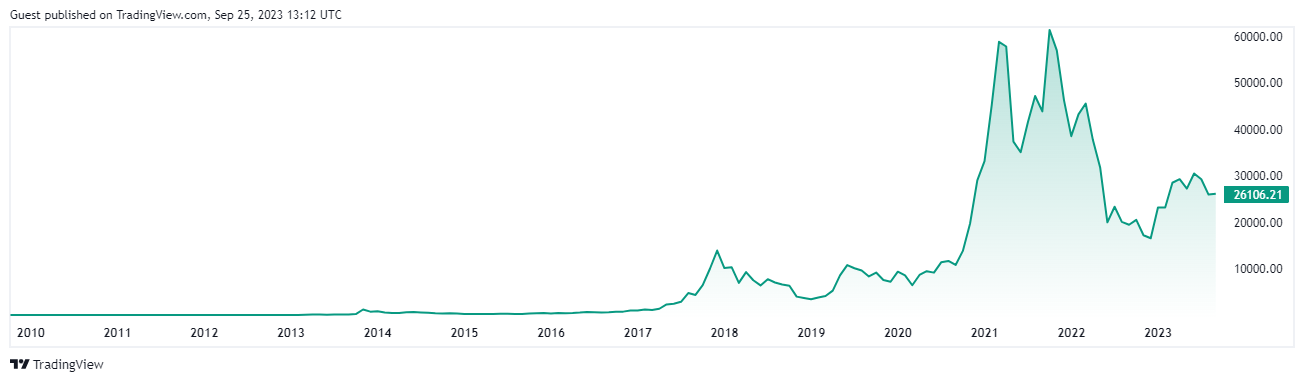
Source & Copyright: TradingView
As the halving approaches, there may be increased media attention, speculation, and hype, which can influence buying behavior and potentially drive up the price in the short term. Conversely, if market sentiment turns negative or if there's a significant external shock (like regulatory crackdowns), it could counteract potential bullish momentum.
Miners may be less inclined to sell their Bitcoin immediately after receiving block rewards, hoping for higher prices due to reduced supply. This could further limit the amount of Bitcoin available in the market, leading to potential price increases.
Other unforeseeable external factors, such as global economic conditions, technological advancements, regulatory changes, or competition from other cryptocurrencies, can influence Bitcoin's price.
By 2024, the cryptocurrency landscape might look quite different. Increased institutional interest and investment in Bitcoin can influence its price. If more institutional investors adopt Bitcoin as a store of value or as "digital gold," it might add further stability and buying pressure.
the cryptocurrency market is maturing, and with it, the reactions to such events as halvings might change. A more mature market might have less volatility, but it could also mean that significant price moves associated with past halvings might become less pronounced.
What About Other Cryptocurrencies?
While Bitcoin holds the title of being the most renowned cryptocurrency, the concept of halving isn't exclusive to it. Many other cryptocurrencies, especially those built on the proof-of-work consensus mechanism, also go through halving events. The primary objective of these halving events in altcoins closely mirrors that of Bitcoin: to regulate the pace at which new tokens are introduced into circulation, consequently managing the supply and potentially fostering scarcity.
For example, Litecoin, one of the earliest offspring or "altcoins" spun off from Bitcoin, also witnesses a halving event approximately every four years. Similar to Bitcoin, the Litecoin network compensates miners with a specific quantity of litecoins for each block appended to the blockchain. However, every four years, this block reward is halved. The most recent Litecoin halving transpired in August 2019, causing the block reward to drop from 25 to 12.5 litecoins. The forthcoming halving, projected to take place in 2023, will further curtail the block reward to 6.25 litecoins.
Another noteworthy example is Bitcoin Cash, a direct derivative of Bitcoin. Owing to its shared history and akin protocol, Bitcoin Cash also experiences a halving event roughly every four years, with the most recent one transpiring in April 2020. This halving action diminished the block reward from 12.5 to 6.25 Bitcoin Cash tokens.
Final Thoughts
As we wrap up our exploration into the world of Bitcoin halving, it becomes evident that this event is more than just a protocol adjustment. The halving ensures Bitcoin remains scarce, predictable, and decentralized, features that set it apart in the vast financial landscape.
Historically, halvings have been pivotal moments, intertwining market dynamics with technology and human behavior. As with any financial endeavor, predicting its precise outcomes remains elusive. Still, one thing is certain: the halving underscores Bitcoin's ever-evolving journey and its profound potential to reshape how we perceive and interact with money.

FAQ
What is the Bitcoin halving?
The Bitcoin halving is an event that happens approximately every four years, where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, reducing the number of new Bitcoins introduced into circulation.
How often does the Bitcoin halving occur?
The Bitcoin halving occurs every 210,000 blocks, which equates to roughly every four years.
How does the halving affect miners?
As the block reward decreases, miners will increasingly rely on transaction fees as an incentive to secure the network.
Are there any risks associated with the Bitcoin halving?
Yes, while the halving can lead to potential price appreciation, it also comes with market volatility. Investors should be aware of the speculative nature of cryptocurrencies and conduct thorough research.
How does the halving affect Bitcoin's overall supply?
The halving ensures that the total supply of Bitcoin will never exceed 21 million, reinforcing its deflationary and scarce nature.
When is the next Bitcoin halving after 2024?
Based on the 210,000 block interval, the next halving after 2024 is expected to occur in 2028, although the exact date will depend on the actual block production rate.



























