
What is Bitcoin?
Our latest in-depth Bitcoin overview will immerse you in the world of the most popular cryptocurrency. Read more to find out what is under the hood of the ground-breaking technology of the Bitcoin network.
What Is Bitcoin? How to Mine, Buy & Use It
Bitcoin (BTC), often labeled as "digital gold," is a pioneering form of digital currency that made its debut in 2009 through a mysterious persona, Satoshi Nakamoto. Transactions with BTC are conducted on the Bitcoin network, which operates on a decentralized network called the blockchain. This means that the network is not controlled or owned by a single entity, making it an open and public platform that is practically impossible to censor. BTC transactions are also auditable and immutable, with each transaction viewable by the public and impossible to undo once executed.
BTC functions as a form of digital money and operates on a network that facilitates secure, online transactions directly between accounts without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or credit card companies, to mediate or verify transactions. This unique feature enables two individuals to send each other BTC from anywhere in the world at any time of the day, without requiring the services of a financial institution or money transfer service. As the first cryptocurrency which kickstarted the global crypto and blockchain phenomenon, BTC remains the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization to this day.
In this article, we'll explore what Bitcoin is, how it works, and how you can get involved in the exciting world of cryptocurrency. So buckle up, and get ready to discover the power of Bitcoin.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is provided solely for informational purposes. Before taking any actions involving cryptocurrencies, it is important to study the legislation in your country. We strongly recommend to do your own research in order to make informed decisions based on your own findings.
Understanding Bitcoin
Bitcoin.org was registered in August 2008, and later in October a person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto introduced a whitepaper outlining a new way of conducting transactions without the need for a trusted third party. This solved the problem of double-spending in digital environments.
In January 2009, the first open-source Bitcoin software client was released, and early adopters were primarily "cypherpunks" who believed in privacy-enhancing technologies for social and political change. As more people recognized Bitcoin's potential, speculation on its future value became a significant driver of adoption.
Over the years, Bitcoin's price and user base grew as regulators clarified its legal status, and Bitcoin exchanges and custodial services were established. This led to further growth and adoption, and now Bitcoin is widely accepted as a legitimate asset class with many high-profile investors showing interest. The blockchain technology powering Bitcoin has also inspired countless other cryptocurrencies and opened up new possibilities for financial innovation.
Bitcoin Price Today
Bitcoin is notorious to be an extremely volatile asset, and its price has been subject to wild swings throughout its history. Bitcoin's first recorded price was in 2010 when it was worth less than a cent. Its price skyrocketed in 2017, reaching almost $20,000 before crashing back down to around $3,000 the following year. Bitcoin price has reached an all-time high in 2021 trading at over 65,000 USD in November 2021. Since then, the price of Bitcoin has been on a rollercoaster ride, with sharp spikes and drops. As of the time of this writing Bitcoin is trading at around 28,000 USD. Bitcoin's price is often affected by a variety of factors, including regulatory changes, political events, media coverage, investor sentiment, and many more.
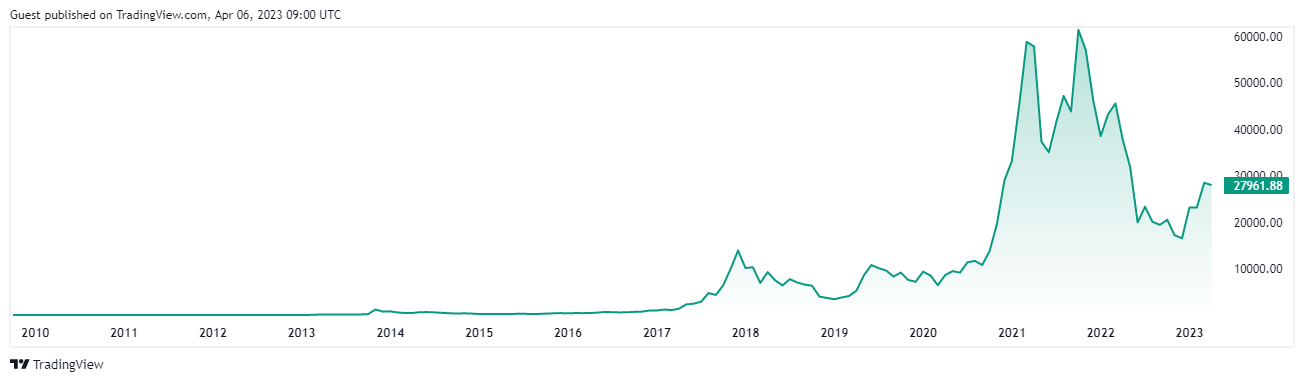
Source and Copyright: © TradingView
Bitcoin's Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin is built on a distributed digital ledger known as a blockchain, which is essentially a linked body of data made up of units called blocks containing information about each transaction.
As soon as a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes accessible to anyone who wishes to view it. Entries are connected together in chronological order, creating a digital chain of blocks. Each block contains information about the transaction, including the date and time, total value, buyer and seller, and a unique identifying code for each exchange.
Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to encrypt the data stored in the blocks on the blockchain. Simply put, transaction data stored in a block is encrypted into a 256-bit hexadecimal number. That number contains all of the transaction data and information linked to the blocks before that block.
For a transaction block to be added to the Bitcoin blockchain, it must be verified by the majority of all Bitcoin holders, and the unique codes used to recognize users' wallets and transactions must conform to the right encryption pattern. These codes are long, random numbers, making them incredibly difficult to produce fraudulently. The level of statistical randomness in blockchain verification codes greatly reduces the risk that anyone can make fraudulent Bitcoin transactions.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Bitcoin network relies on a Proof of Work consensus mechanism. At the core of the PoW is the concept of mining, a process by which new Bitcoin is created and transactions are verified.
When a transaction takes place on the blockchain, information from the previous block is copied to a new block with the new data, encrypted, and the transaction is verified by validators, called miners.
When a transaction is verified, a new block is created, and the miner(s) who verified the data within the block is rewarded with a newly created Bitcoin.
Source and Copyright: © bitcoin.org
To validate transactions, miners in the Bitcoin blockchain network attempt to verify the same transaction simultaneously. Miners attempt to solve the nonce, a four-byte number included in the block header. The block header is hashed or randomly generated repeatedly by the miner until it meets a target number specified by the blockchain. When the block header is solved, a new block is created for more transactions to be encrypted and verified.
If you're looking to get into Bitcoin mining, there are several things you need to consider before diving in. First and foremost, the days of mining Bitcoin on a personal computer are long gone. Nowadays, mining Bitcoin requires specialized hardware and software.
The reason for this is that you're competing against a vast network of miners. While it's still possible to mine Bitcoin on a personal computer with newer hardware, the chances of successfully mining a block individually are incredibly slim.
One option is to join a mining pool, where groups of miners combine their computational power to increase their chances of mining a block. However, the rewards for mining in a pool are significantly decreased because they are shared among the members.
If you have the financial means, you could also consider purchasing an ASIC miner, which is specifically designed for mining Bitcoin. Keep in mind that there are additional costs such as electricity and cooling to consider if you decide to go this route.
When it comes to mining software, there are many options to choose from, it is essential to do your research and choose a reputable mining pool with fair reward payouts and reasonable fees. Reading reviews from other miners can also give you a better idea of which pool to join.
How Do You Buy Bitcoin?
You must first select a Bitcoin exchange or marketplace to purchase from. After choosing an exchange, you must register an account and authenticate your identity. Typically, the process requires submitting personal information and identity papers.
Once your account has been validated, you can fund it via bank transfer or credit/debit card. Once the funds have been deposited into your account, you are free to purchase Bitcoin at the current market price.
After acquiring Bitcoin, you may choose to transfer it to a secure wallet under your control. This guarantees that you have complete control over your cash and that they are not vulnerable to potential security breaches on the exchange.
A Bitcoin wallet has a public key and a private key, which function similarly to an email address and a password. The public key unlocks a virtual vault containing your Bitcoin, but only the owner of the private key may access the funds.
As long as you take the required care to protect your private key and use a trustworthy exchange or wallet provider, purchasing and keeping Bitcoin can be a straightforward and secure process.
How Is Bitcoin Used?
Initially designed as a peer-to-peer payment method, Bitcoin has grown to become a widely accepted currency that's used in a variety of ways.
Payment
One of the most popular uses for Bitcoin is as a means of payment. From huge organizations to small and medium-sized enterprises, an increasing number of businesses accept Bitcoin as a digital payment. Governments are also gradually adopting Bitcoin, with El Salvador becoming one of the first to make it an official currency. Presently, one of the most convenient methods to utilize Bitcoin is to put it onto a cryptocurrency debit card and then use it to purchase products and services or withdraw cash from ATMs.
Investment and speculation
Many investors buy Bitcoin with the idea of benefitting from its rising value over time, either by retaining it for the long term or by trading it on cryptocurrency exchanges. As previously indicated, Bitcoin's price volatility makes it a popular target for speculators seeking to make a quick profit. Some investors utilize technical analysis and market patterns to attempt to forecast Bitcoin's future price moves, but others simply purchase Bitcoin and hold it for the long term.
Institutional investors and hedge funds have entered the Bitcoin market in recent years, driving up demand and pushing the price even higher. This has raised the mainstream media's interest and focus, as well as the scrutiny of regulators and legislators.
Bitcoin vs. Fiat Money
| Criteria | Bitcoin | Fiat money |
| Control and regulation | Decentralized network, created by individuals and organizations known as miners | Centralized, regulated by governments and central banks |
| Security | Transactions are secured through cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanism | Relies on physical security measures and government guarantees |
| Transparency | Transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain ledger | Limited transparency, transactions are not publicly visible, but can be traced by authorities |
| Portability | Can be easily transferred across borders without currency exchange fees | Subject to currency exchange rates and government regulations |
| Volatility | Highly volatile, subject to speculation and market forces | More stable, subject to government policies and economic conditions |
| Accessibility | Accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a wallet | Requires a bank account or physical currency |
| Acceptance | Increasing acceptance by businesses and individuals, but still limited compared to traditional fiat money | Widely accepted by businesses and individuals |
| Regulation | Currently, there is limited regulation and legal clarity in many jurisdictions | Heavily regulated by governments and subject to legal frameworks |
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin
Bitcoin, like any investment, comes with its own set of risks that must be considered before investing. The primary concerns associated with investing in Bitcoin include hacking, fraud, and the lack of regulation.
While the security of blockchain technology makes hacking very difficult, there is still room for scammers to take advantage of unsuspecting investors. These criminals may ask for payment in Bitcoin or offer unrealistic ways of earning more Bitcoin, so it is crucial to be vigilant and only buy Bitcoin through reputable and verified exchanges.
The volatility of the cryptocurrency market is another risk associated with investing in Bitcoin. Its price can fluctuate greatly and without warning, which can result in significant financial losses for investors who are not prepared for such market changes.
Additionally, governments and regulatory bodies around the world have varying views on Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. Changes in regulations or the introduction of new laws could affect the price and adoption of Bitcoin.
Regulating Bitcoin
With increasing Bitcoin acceptance comes the necessity for regulation. A rising number of countries are building regulatory frameworks to handle issues like as consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism funding (CTF), as well as taxation.
In the United States, for instance, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has assumed a more active role in regulating cryptocurrencies, focusing on whether cryptocurrencies should be categorized as securities. The Chinese government has prohibited cryptocurrency trading and initial coin offerings (ICOs).
The Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) rule is a new legal framework for cryptocurrencies suggested by the European Union. The regulation would create standards for the issuing and trade of cryptocurrencies and require issuers to register with the appropriate authorities.
While there is still a significant deal of legislative ambiguity around cryptocurrencies, an increasing number of nations are taking action to address the problems brought by these new digital assets.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is a digital asset that has transformed the financial landscape in unprecedented ways. Its decentralized nature facilitates peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a trusted intermediary, making it an innovative solution for conducting transactions across borders or outside of traditional banking systems. However, its significant price fluctuations have also made it a volatile asset, leading to increased speculation and investment activity.
Powered by a blockchain network that employs intricate encryption methods to secure transactions, Bitcoin has opened the door for many other cryptocurrencies to emerge. Its impact on the world of finance is expected to endure for many years. Nonetheless, whether investing in Bitcoin is appropriate for an individual depends on their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and overall financial situation. Therefore, it is essential to carefully evaluate these factors before investing.
FAQ
Who invented Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was invented by an unknown person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
How Does Bitcoin Make Money?
Bitcoin miners earn money by verifying transactions on the network and receiving newly created Bitcoin as a reward.
Can Bitcoin be Сonverted to Сash?
Yes, Bitcoin can be converted to cash on a cryptocurrency exchange or through a Bitcoin ATM.
How Long Does It Take to Mine One Bitcoin?
The time it takes to mine one Bitcoin varies depending on the mining hardware and the difficulty of the network, but it currently takes an average of 10 minutes to mine one block and receive the Bitcoin reward.
How Many Bitcoins Are Left?
As of 2023, around 19 million bitcoins have been mined out of the maximum cap of 21 million.
Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
Bitcoin has been a volatile investment with the potential for high returns but also high risk, so it is important to carefully consider it before investing.
Is Bitcoin Safe?
Bitcoin can be stored and transferred safely, but there have been instances of exchange hacks and thefts, so it is important to take precautions to protect your Bitcoin.
What are the Problems with Bitcoin?
Bitcoin has faced criticism for its energy consumption, scalability issues, and potential for use in illegal activities.


























