
What is Blockchain?
You've probably already heard about blockchain technology. But what is it all about? Our in-depth guide will delve into the underpinnings of this cutting-edge technology. Discover why blockchain has had such a profound impact on the modern world and how it can potentially transform it
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is a term that has been gaining popularity in recent years, but it's still a relatively new concept for many people. Whether you are familiar with the concept or not, blockchain technologies are already all around us and shaping the modern financial world.
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed digital ledger maintained by computers all around the world that records transaction activity, stores data, and allows for the exchange of value without the need for intermediaries or central authorities. The technology uses cryptographic protocols to secure the data and ensure its immutability.
The technology is the foundation of the entire cryptocurrency, Web3, and smart contracts ecosystem providing a trust-minimized and permissionless way to interact and exchange value without intermediaries.
Blockchain networks operate through systems of aligned incentives, and they require a community of users, node operators, developers, and miners to function correctly. The community is motivated by rewards like newly minted cryptocurrency or transaction fees, which also secure the network from criminal or fraudulent activity.
The concept of blockchain dates back to the early 1980s, but the technology started to gain widespread attention in 2009 after the world saw the birth of Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the first and most well-known application of blockchain technology, learn more about it. Ethereum, launched in 2015, has evolved the technology further and kick-started such industries as DeFi and NFT.
The reason why blockchain technology has grown so popular is because of its ability to facilitate the faster movement of transactions, saving both time and money. Record keeping of data and transactions is a crucial part of the business. In the past, financial records were kept in paper ledgers that were kept at financial establishments. Audits of traditional ledgers were possible, but only for an exclusive few. Blockchain took these ideas and made them more accessible by reducing the opacity surrounding the handling of information, specifically transaction data.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology provides a structure that stores transactional records in several databases in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes.
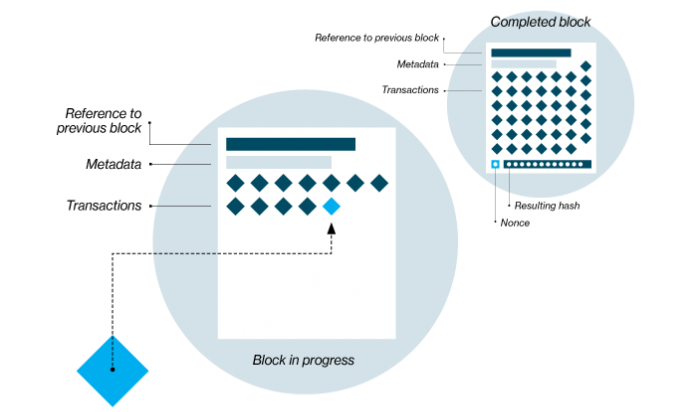
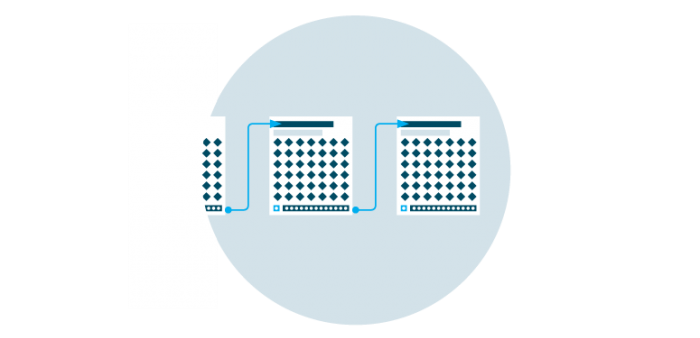
At its core, blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable link between them.
Each block in a blockchain contains a certain amount of data, and it is linked to the previous block chronologically, forming a virtual chain of blocks. A blockchain can be thought of as a train with multiple carriages, each containing a set amount of data. Each block contains a timestamp, making it clear when the data was recorded and stored.
Source and Copyright: © technologyreview.com
This chain of blocks forms a distributed ledger, which is stored on a network of computers or nodes. Nodes are computers or devices that are part of the network and hold a copy of the blockchain ledger which ensures that the data is not lost even if some of the nodes go down. Each node in the network can perform various functions, such as validating transactions, adding new blocks to the chain, and ensuring consensus. This enables a secure and transparent system for recording and verifying transactions. Simply put, blockchain is essentially a distributed list of transactions that is constantly updated and reviewed.
How Does a Blockchain Work?
One of the key features that underpin blockchain technology is its consensus mechanism. This mechanism ensures that all the nodes in the network agree on the information stored in the ledger. The consensus mechanism helps to prevent fraud and ensure that the data in the blockchain is secure and accurate.
Proof of work and proof of stake are the two major consensus mechanisms for blockchain networks to verify new transactions, add them to the blockchain, and create new tokens/coins. Proof of work, first pioneered by Bitcoin, uses mining to achieve those goals. Proof of stake — which is employed by Ethereum and others — uses staking to achieve the same things. Let’s dive deeper into both concepts.
Proof of Work
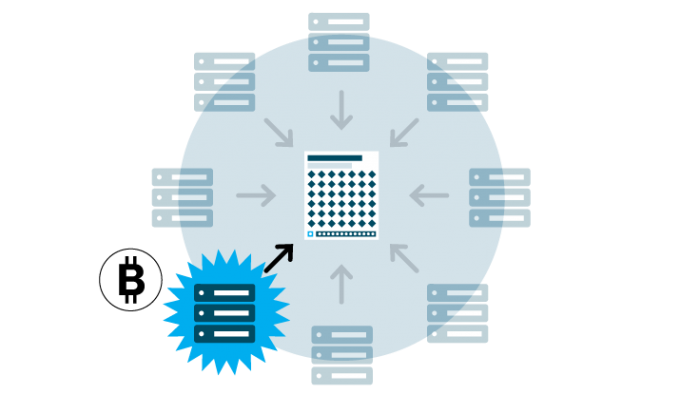
PoW is a consensus mechanism that requires network users, known as "miners," to devote computing power to complete a task. In the Bitcoin protocol, for example, miners compete using their computers to generate random, fixed-length codes called hashes. They create these hashes by running inputs at random through a cryptographic hashing algorithm. The miner who generates a hash with the same or more zeros at the front compared to the target hash gains the right to propose a new block of transactions to join the blockchain. If the proposed blockchain is valid, the miner receives a block reward for their efforts.
Source and Copyright: © technologyreview.com
Once a new block of transactions has been proposed by the winning miner, the remaining miners in the network then independently verify those transactions. By requiring all users in the network to independently confirm proposed transactions before they are finalized, it's nearly impossible to double-spend one's balance. After the mining competition for each new block ends, it then starts all over again based on the block time each protocol is programmed to follow.
Source and Copyright: © technologyreview.com
Proof of Stake
In contrast, PoS uses a different series of incentives to ensure that network participants behave honestly. In a PoS system, network participants purchase and lock away a protocol's native tokens for the chance to receive rewards for validating blocks of transactions. This process is known as staking. Participants with more tokens staked are more likely to be chosen to validate a new block, but there is still an element of randomness to the selection process, similar to a lottery system.
Instead of competing with each other to solve cryptographic puzzles, PoS validators are incentivized to work together to validate transactions accurately. Validators who act dishonestly, such as proposing invalid blocks, are penalized by losing a portion of their staked tokens. PoS is less energy-intensive than PoW. PoS systems require far less computational power, and the energy consumption is significantly lower.
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are the most common consensus mechanisms, however there are a number of other alternatives. Many of these options combine components from various other encryption and consensus mechanisms. The list of available consensus mechanisms is constantly growing and changing.
Types of Blockchain Networks
Nowadays, there are different types of blockchain networks such as public, private, and consortium.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to everyone, enabling users to view, send transactions and participate in the consensus process, making them decentralized. Cryptoeconomics secures public blockchains using proof-of-work or proof-of-stake. These blockchains provide transparency, no third-party verification, and anonymity to their users. However, they require significant computing power, have little privacy for transactions, and inadequate security.
Private Blockchains
On the other hand, private blockchains, also known as managed blockchains, are permissioned blockchains administered by a single entity. The central authority in a private blockchain decides who can be a node and what functions they can execute. Private blockchains provide data confidentiality, higher privacy, compliance, and stability. However, public access to private blockchains is restricted, making them only partially decentralized. They are more susceptible to fraud and bad actors.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are permissioned blockchains that are administered by a consortium of organizations rather than a single institution, providing more decentralization than private blockchains, resulting in increased security. The consortium blockchain is supervised by one party, but it is protected against dominance. It has a high level of privacy, no transaction fees, and flexibility. However, setting up consortiums can be challenging and time-consuming, with the risk of antitrust violations
Blockchain Decentralization
The key reason that organizations use blockchain technology, instead of other data stores, is to provide a guarantee of data integrity without relying on a central authority. This is called decentralized trust through reliable data. Decentralization in blockchain means that there is no single point of failure in the network.
Every node in the network carries a copy of the data, with any data changes going through validation by other nodes. This process is crucial for preventing any malicious activity like fraud or hacking. As the majority of nodes must approve any data change, this brings reliability and trustworthiness to data handling.
In a decentralized network, all participants can see and verify every transaction. This means that anyone can check the integrity of the network, and there is no need to trust a central authority to ensure that the system is functioning correctly.
Apart from ensuring data integrity, decentralization promotes innovation. It paves the way for developers to build new applications over existing blockchain platforms with ease.
Moreover, this decentralized feature promotes inclusivity, and even people who lacked access to financial services earlier can now transact via blockchain technology without banks or payment processors. This phenomenon opens up new possibilities for financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
All in all, decentralization has made blockchain technology a popular choice in various industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. In finance, blockchain is utilized for secure and transparent transactions, while in healthcare, it is used for secure storage of patient data. Finally, in supply chain management, blockchain is used for tracking and verifying the authenticity of products from the manufacturer to the end consumer.
Transparency
Due to the decentralized nature of most blockchain networks, all transactions made on them can be viewed transparently using a personal node or blockchain explorers like Etherscan, which enable anyone to view live transactions. In its simplest form, transparency in blockchain refers to the ability to view and verify all transactions that occur on the blockchain network. This means that you could track your tokens or coins wherever they go along with wallet addresses.
If a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is there for everyone to see, and any attempt to tamper with it would be immediately noticeable. This makes it much more difficult for bad actors to engage in fraudulent activities like double-spending, which can be a major issue in traditional financial systems.
Because all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, it is possible to trace the history of a particular asset or transaction back to its origin. This is particularly useful in situations where there is a need to investigate suspicious activities or transactions. For example, if an individual is suspected of engaging in money laundering, it would be possible to trace their transactions on the blockchain and identify any suspicious patterns.
However, it is important to note that transparency in a blockchain does not necessarily mean that all information is available to everyone. While all transactions are visible on the blockchain, the identities of users are kept private through the use of public-private key pairs. This means that while the transactions themselves are transparent, the identities of the users involved are not necessarily public knowledge.
Is Blockchain Secure?
Blockchain technology has garnered a reputation for its security measures, which have made it a less attractive target for hackers attempting to tamper with the data on the blockchain. The security measures employed by blockchains rely heavily on cryptography, particularly cryptographic hashing functions, to achieve data security. These hashing functions generate unique identifiers for data blocks, which are then linked together to create a chain of linked blocks, thereby ensuring the immutability of transaction records and making it extremely difficult for anyone to alter the data stored in a blockchain.
Public and Private Keys
Cryptography not only provides protection for transaction records on ledgers, but also plays a crucial role in securing crypto wallets through the use of public and private keys. In blockchain networks, public and private keys are used to verify and authenticate transactions. Public keys, derived from the private key, serve as a public identifier that can be used to receive payments from others and are shared freely within the network to identify an account or address.
In contrast, private keys are a secret and should only be known to the account owner. Private keys are used to digitally sign transactions, proving that the sender is authorized to send funds from that account. Without the private key, accessing or spending funds in that account would be impossible.
Private keys can be stored in a variety of ways, ranging from digital wallets to hardware wallets, and the security of the private key is crucial to maintaining the security of the account. Therefore, users must take steps to ensure that their private keys are kept safe to prevent unauthorized access or loss of funds.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain
Blockchain is the underlying technology of the digital currency Bitcoin, but Bitcoin is not the only blockchain-based distributed ledger system on the market. In fact blockchain has found many use cases beyond Bitcoin. Bitcoin transmits monetary value between users, whereas blockchain can be used to transfer a variety of assets, such as information or property ownership rights. There are currently tens of thousands of projects exploring the many ways in which blockchain technology can be used.
Blockchain vs. Banks
Throughout the course of human history, banks have stood as pillars of the financial system, serving as key intermediaries between various parties. However, the emergence of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) has sparked a paradigm shift in the financial landscape, presenting a challenge to the established banking model.
Centralization
One of the most prominent disparities between blockchain technology and banks is the issue of centralization. Unlike banks, blockchain technology is decentralized, operating without the need for a central authority to process and record transactions. While centralization provides greater control and supervision, it lacks transparency and is vulnerable to corruption, fraud, and other forms of harmful activities.
Speed of transactions
When it comes to transaction processing speed, blockchain technology's design is geared towards speed and efficiency. Transactions are executed within a matter of seconds or minutes, regardless of the size or complexity of the transaction. On the other hand, banks can be quite slow, with transactions taking days or even weeks, particularly for cross-border transactions.
Accessibility
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have the potential to break down the barriers to widespread financial inclusion, particularly for individuals and communities that are currently underserved or excluded from the traditional banking system. Banks are often exclusive, with high fees, strict eligibility criteria, and a lack of accessibility in many regions and communities.
In today's global economy, the benefits of blockchain technology are especially appealing. The rise of DeFi applications built on blockchain technology has given birth to a novel financial services ecosystem that can bypass traditional banks and financial institutions, enabling peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
Nevertheless, the adoption of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies carries a set of risks and challenges, such as regulatory ambiguity, market volatility, and the possibility of fraud and money laundering. Moreover, the traditional banking model still possesses significant advantages, including stability, trust, and an extensive history of providing financial services to customers for centuries.
How Are Blockchains Used?
Blockchain technology is useful for many industries, including finance, supply chain, real estate, and gambling. It uses self-executing code called smart contracts, which are stored on an unchangeable digital ledger. Smart contracts help companies and individuals avoid the expense of engaging third parties for routine business.
Blockchain technology is great for payments. Bitcoin, bitcoin cash, and litecoin are examples of cryptocurrencies that use blockchain technology to process payments. Blockchain payments are efficient and accessible worldwide. Blockchain technology is also useful in industries that need secure ways of owning and controlling data. Healthcare, the Internet of Things, and digital identity industries are using blockchain to create cutting-edge solutions.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
As it was mentioned before blockchain has numerous advantages over traditional finances and here are the key takeaways:
Constant: The global nature of blockchain networks enables transactions to occur 24/7.
- Fast: Transactions are sent directly between sender and receiver without the need for intermediaries, resulting in speedy processing.
- Secure: The distributed network of nodes underlying blockchain provides collective security against hacks and outages, ensuring the safety of transactions.
- Inexpensive: The absence of centralized intermediaries results in lower costs for blockchain operations.
- Tamper-proof: Once data is timestamped and recorded on the blockchain, it is impossible to modify, making it transparent and secure against fraudulent activity. Public blockchain networks allow for anyone to view transaction records.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Scalability is one of the greatest obstacles confronting blockchain technology. As more transactions are added to the blockchain, the network may become slower and more difficult to maintain.
The lack of regulation and standardization in the blockchain space is another cause for concern. Due to the proliferation of platforms and protocols, it can be challenging to ensure interoperability and consistency across blockchain networks.
The decentralization of Blockchain increases privacy and secrecy, which regrettably makes it attractive to criminals. It is more difficult to monitor illicit transactions on blockchain than through name-attached bank transactions.
Concerns also exist regarding the environmental impact of blockchain technology. The energy-intensive validation of transactions on certain blockchain networks can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other negative environmental effects.
The Bottom Line
Blockchains have quickly become an integral part of our daily lives, influencing the ways in which we work, communicate, and store and access digital data. Although the technology has not yet settled on a unified set of standards, and its full significance is still being explored, one thing is certain: blockchain is not going away.
The widespread implementation and investigation of this technology's multiple practical applications contributes to its rising popularity. It has already been put to good use in the real world.
Blockchain is a promising technology yet with limited mainstream usage at this time due to uncertainty about how governments will regulate it. Despite these hurdles long with transaction limits and energy costs, in the coming years, blockchain technology will likely continue to transform our lives, much like the internet did in the past.
FAQ
What Is a Blockchain in Simple Terms?
A blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and tamper-proof way.
Why is blockchain important?
Blockchain is important because it allows for secure and transparent transactions without the need for a central authority or intermediary.
How Many Blockchains Are There?
There are thousands of blockchains, but the most well-known are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
What's the Difference Between a Private Blockchain and a Public Blockchain
The main difference between a private blockchain and a public blockchain is that private blockchains are permissioned, meaning that only certain parties have access to participate and verify transactions, while public blockchains are permissionless and anyone can participate.
Who Invented Blockchain?
Scott Stornetta and Stuart Haber are credited with inventing the blockchain concept, they were even mentioned in the Bitcoin white paper. However, the first blockchain was conceptualized by a person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008.

























