
What Is Venom Blockchain?
Dive into the Venom Blockchain - a Layer 0 solution with unique features. Discover how it solves the common blockchain problems and what is behind its architecture.
What is Venom Blockchain?
Venom is a Layer 0 blockchain network, integrating dynamic sharding technology and utilizing a proof of stake (PoS) consensus model.
This blockchain platform is developed with the goal of offering a scalable and convenient infrastructure suitable for developing DeFi, NFT, and gaming applications. The Venom Network is governed by the non-profit Venom Foundation, located within the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM).
How Does Venom Blockchain Work?
Venom is a layer-0 blockchain, which uses a technique called dynamic sharding to improve its scalability. Being a layer-0 blockchain means it acts as the primary foundation where layer-1 blockchains can be developed, offering a solution to the rigidity found in networks with a monolithic architecture like Bitcoin by avoiding common bottlenecks.

Unlike traditional monolithic blockchains, where everything is built on one chain, Venom uses a masterchain to validate and execute transactions. This masterchain, being at the heart of Venom, is responsible for coordinating and communicating with workchains and shard chains, which are Venom’s layer-1s. This structure allows each chain to function independently, eliminating the need for transactions to pass through a single consensus process or limiting the size of data for each transaction.
Here’s how Venom processes transactions:
- A transaction is initially submitted to a shard chain.
- This shard chain validates the transaction and incorporates it into a block.
- The block is forwarded to the masterchain.
- The masterchain validates this block and integrates it into the blockchain.
- Finally, the transaction is executed on a workchain.
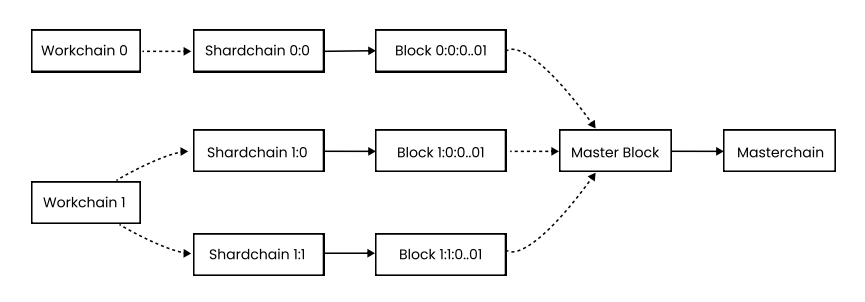
Source & Copyright: Venom Whitepaper
A notable aspect of Venom is its dynamic sharding protocol. This system enables the blockchain to divide into smaller, independently operating segments. When there's a high demand for processing smart contracts, validators form smaller shard chains to process transactions simultaneously. When the demand decreases, these shard chains recombine into the masterchain, enhancing the processing speed of transactions without increasing the fees or the need for more computing power.
Venom also uses Threaded Virtual Machine (TVM), allowing the running of smart contracts in various programming languages, such as Rust and Go. For instance, Ethereum’s EVM is only compatible with Solidity. This feature lets developers write smart contracts in their preferred languages, which is expected to boost the development of unique decentralized applications (DApps) within the Venom ecosystem.
Venom Ecosystem Overview
the Venom Ecosystem include the following products with the plans to deploy more in the future:
Venom Wallet: A secure, non-custodial wallet featuring multisig account support and compatibility with Ledger for enhanced asset safety.
VenomStake: Offers a dedicated platform for the staking of VENOM tokens, aiming to maximize reward opportunities for its users.
VenomBridge: Enhances the interoperability across blockchains, enabling smooth transactions between different chains.
Web3World: Acts as Venom's own decentralized exchange (DEX), supporting the exchange of assets, providing liquidity, and enabling farming within the ecosystem.
Oasis Gallery: A marketplace for distinctive digital assets, meeting the growing interest in NFTs and digital collectibles.
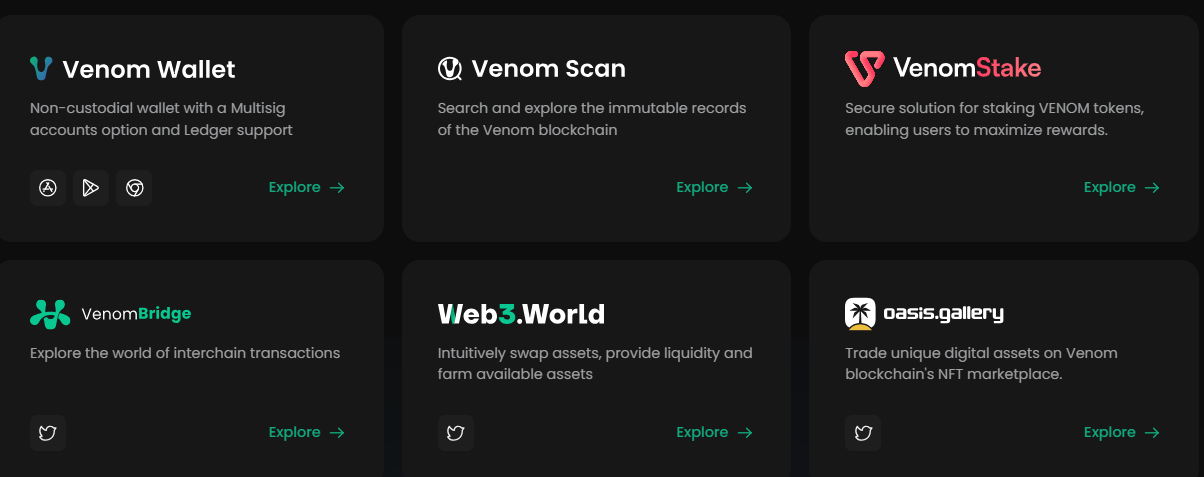
Source & Copyright: Venom Foundation
Venom Tokenomics
VENOM is the native token of the Venom blockchain. It can be divided into smaller denominations such as NanoVENOM, MicroVENOM, and MilliVENOM. It serves various functions within the ecosystem, including compensating transaction fees to support network operations by validators, enhancing network security via Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanisms, and enabling network participants to support validators through staking. Initially, the Venom blockchain will introduce a total supply of 7.2 billion VENOM tokens, with just 15% becoming available initially. The allocation of these tokens will proceed as follows:
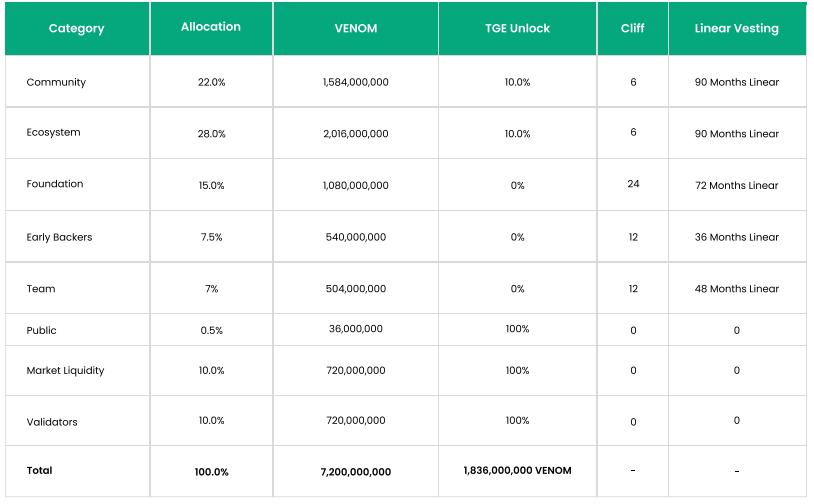
Source & Copyright: Venom Whitepaper
Team Behind Venom
The project's core development team include:
Peter Knez: Ex-Chief Investment Officer at BlackRock and Barclays Global Investors (BCI).
Mustafa Kheriba: Board member at several prestigious institutions, including Mirabank and Australian Gulf Capital, as well as Evrensel Capital Partners.
The Venom team received support from investment funds and partners such as Venom Ventures, Iceberg Capital, Developer DAO, Hacken, Hub71, and DAO Maker.

Final Words
At this point the Venom Blockchain presents itself as a legitimate project within the Layer 0 blockchain space. Although it's still early days, given the network's recent launch, the promising suite of applications and robust technology suggest a solid foundation for growth. Our team will continue to monitor the developments around Venom and keep you updated on its progress.



























