
What is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking is a method that transforms staked assets into forms that are liquid and tradeable. In this article, we'll delve into the popular concept of liquid staking within the crypto world, explaining how it operates and outlining its benefits.
Liquid staking is a method that transforms staked assets into forms that are liquid and tradeable. It enables cryptocurrency holders to contribute to the security of PoS blockchain networks while maintaining the flexibility to use their staked assets' value for various activities, such as lending and trading.
In contrast to traditional staking, which freezes a user’s tokens until they are unstaked, liquid staking provides ongoing access to the value of staked assets, which can be used in various decentralized finance applications or other web3 protocols. The primary advantage of liquid staking is that it liberates assets that would otherwise be locked away.
Up to date, liquid staking remains the largest DeFi category in terms of Total Value Locked (TVL), amounting to $46B+ per DeFiLlama.
In this article, we'll delve into the popular concept of liquid staking within the crypto world, explaining how it operates and outlining its benefits.
But first things first. To understand liquid staking, it's first necessary to understand staking itself.

What is Staking?
Traditional staking is a foundational concept in Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain systems. In PoS networks, staking involves locking up a certain amount of a cryptocurrency (staking) to participate in the network's operations, such as validating transactions, maintaining security, and governance. Validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake. This staking helps secure the network, and in return, stakers earn rewards.
Here’s how the staking works in traditional PoS system:
- Holders lock their tokens in a smart contract to participate as validators in the network.
- Depending on the PoS network, validators may be chosen randomly or based on the size of their stake, with higher stakes generally increasing the likelihood of being selected to validate blocks and transactions.
- Validators earn staking rewards, which are proportional to the amount staked and the length of time tokens are locked.
If a validator wishes to withdraw their stake, there is typically an "unbonding" period during which the staked tokens cannot be moved. This period can vary significantly across different blockchains and serves to secure the network by preventing sudden, large withdrawals which could undermine the network’s stability.
Limitations of Traditional Staking
One of the major hurdles in staking on proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains is illiquidity. Once users commit their tokens to staking, they are locked and inaccessible, which restricts their ability to generate further yields from other decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols during the lock-up period.
Moreover, the high entry requirements, including substantial costs associated with operating a node and the complexity involved in setting up a validator, discourage many users from engaging in PoS staking.
Here is where liquid staking comes into play.
What is Liquid Staking and What are Liquid Staking Derivatives?
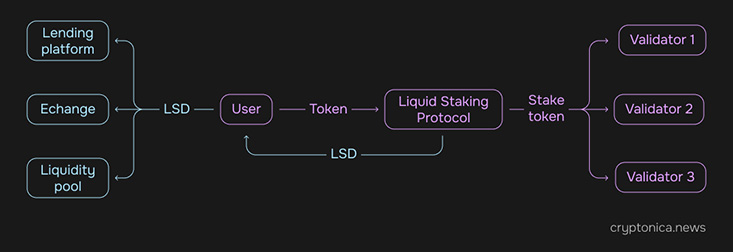
Similar to traditional staking, liquid staking involves users locking their tokens into a smart contract on the liquid staking platform. The key difference, however, lies in the subsequent steps.
Once tokens are locked in, the liquid staking provider stakes these tokens on behalf of the token holder. In exchange, the user receives Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSD), a tokenized version of their staked assets. These derivatives mirror the value of the staked tokens and offer the flexibility to be traded, sold, or utilized in other DeFi protocols, thus maintaining liquidity for the user even as their original assets continue to be staked.
For instance, a user might deposit ETH into the Lido staking protocol and receive stETH (staked ETH) in return. This stETH reflects your staked ETH and can be used just like any other ERC-20 token. For example, it could then be deposited into a lending platform like Aave to generate additional yield. In essence, liquid staking enhances the traditional staking model by providing liquidity to staked tokens, making them more versatile and usable across various financial applications.
How Does Liquid Staking Work?
If the concept is still unclear let’s try to describe how the process unfolds in practice.
Users begin by depositing their cryptocurrency tokens into a liquid staking service. This service could be a smart contract or a platform that specializes in liquid staking solutions. Popular liquids staking protocols are Lido Finance, Rocket Pool, Frax and many more.
Upon staking their tokens, users receive liquid staking derivative tokens in return. These tokens represent the staked assets but are liquid and can be used independently of the staked capital. The ratio of issued derivative tokens to staked tokens can be 1:1 or vary based on the platform's specific mechanism.
The derivative tokens can be used in various DeFi applications:
- Buy or sell the derivative tokens on exchanges.
- Use them as collateral for borrowing in DeFi lending platforms.
- Provide liquidity to a pool in a decentralized exchange and earn transaction fees.
While the original tokens are locked and staking within the PoS network, they continue to earn staking rewards. These rewards increase the value of the derivative tokens, which are pegged to the staked assets plus any accrued rewards.
Centralized versus Decentralized Liquid Staking Platforms
Platforms such as Coinbase and Binance represent centralized methods for liquid staking, where users hand over their cryptocurrency assets to a centralized entity that takes on the role of both custodian and staking operator.
These centralized liquid staking platforms are convenient for users who might not have the technical knowledge required to engage with liquid staking themselves. However, they also carry counterparty risks related to the centralized nature of these platforms, such as the potential for insolvency, mismanagement, or issues arising from regulatory changes.
In contrast, decentralized liquid staking protocols like Lido Finance and Rocket Pool remove single points of failure by allowing users to maintain control over their assets without relying on centralized intermediaries. Nevertheless, this form of staking requires users to possess some technical expertise in web3, including an understanding of decentralized protocols and smart contracts. Additionally, users must manage factors such as gas fees, the risks inherent in smart contracts, and network congestion that might impact their staking activities.
Is Liquid Staking Safe?
Liquid staking, while offering numerous benefits, also introduces several risks that participants should consider. The main risk associated with liquid staking is the potential depegging of the value of the derivatives from the value of the original tokens.
The issue with these derivatives is that they are not algorithmically bound to the original tokens. Instead, they are freely traded on the market, and their prices are solely determined by market dynamics. This means that in a bear market or during a liquidity crisis, these derivatives might sell for significantly less than the value of the original tokens.
For instance, derivatives in the Terra ecosystem almost simultaneously depegged when the system collapsed, resulting in substantial financial losses for investors.
When a significant depeg occurs, the immediate consequence is practically losing access to the original tokens. Even if one could exchange their derivatives for the original staked assets, the value of these assets would likely have decreased significantly, posing a serious risk that does not typically exist with traditional staking.
Additionally, liquid staking can inadvertently lead to centralization. Liquidity pools, which accumulate large quantities of staked tokens, can delegate these tokens to specific validators. If such a pool grows large enough, it might centralize the governance of the blockchain and potentially take control of it.
FAQ
What is liquid staking?
Liquid staking is a mechanism in Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains that allows cryptocurrency holders to stake their assets and receive liquid tokens in return.
How does liquid staking differ from traditional staking?
Unlike traditional staking, where staked assets are locked and illiquid, liquid staking provides holders with derivative tokens that are tradeable and usable in other financial activities.
What are derivative tokens in liquid staking?
Derivative tokens in liquid staking are digital assets issued to stakers that represent the original staked assets plus accrued rewards. These tokens can be traded, used as collateral, or used to participate in other DeFi applications.
What happens to my original staked tokens when I engage in liquid staking?
The original tokens are locked in a staking contract and used to secure the network, while you receive derivative tokens that represent your staked assets and any rewards they earn.
Is liquid staking available for all cryptocurrencies?
Liquid staking is primarily available for cryptocurrencies that use a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Not all PoS cryptocurrencies offer liquid staking options, but it is becoming more common as the DeFi sector grows.


























