
What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work
This guide explains what Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is, how it works, and the potential risks and rewards associated with investing in DeFi projects. Read on to learn more!
Decentralized Finance, often abbreviated as DeFi, has been making waves in the world of Finance and technology. It represents a powerful disruption to the traditional systems, embodying the promise of blockchain technology to decentralize and democratize access to financial services. In contrast to the centralized banking systems, DeFi operates on public blockchains, mainly Ethereum, offering a transparent and open network. It utilizes cryptographic tools and smart contracts to allow individuals to manage and trade their cryptocurrency funds, bypassing central authorities like governments and banks. This guide aims to provide you with an understanding of what DeFi is, how it works, and the potential benefits it holds for the future of Finance. So, let's get started!
What Is DeFi?
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi for short, is a financial system built on blockchain technology that uses smart contracts and other cryptography tools to enable users to participate in risk-free transactions.
Doing so eliminates the need for middlemen like banks or governments, instead relying on code to facilitate transactions between users. It also brings considerable transparency to the system, allowing participants to keep track of their transactions and assets at all times. As such, it provides a much more secure and trustless way to manage digital assets, enabling users to borrow, lend, trade, and access financial services without relying on any external entity. Moreover, it allows users to earn interest on their crypto investments, offering lucrative returns. People can access their assets from anywhere and anytime, with transactions executed quickly and securely.
How Does DeFi Work?
The core of DeFi is built on blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum. Smart contracts are used to facilitate transactions between users in an automated and transparent manner. In the Blockchain network, there are no intermediaries or middlemen. This is made possible by the use of a consensus algorithm that allows all participants to agree on any transaction before it is executed.
For example, when a user wants to borrow funds from another user on the network, they enter into a smart contract that outlines the terms of the loan. This process allows them to access capital quickly without relying on any intermediary or external entity. Once the loan is paid off, the funds are automatically transferred back to their original owners.
Moreover, in blockchain, every transaction is recorded on the ledger and can be seen by all participants. This provides full transparency to users, allowing them to track and monitor their assets at all times.
DeFi also relies on various other cryptography-based tools, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and non-custodial wallets.
Through these tools, users can access financial services and transact with each other in a secure environment.
What makes up decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
At its core, DeFi encompasses a variety of decentralized applications (DApps), protocols, and technologies that work together to create a new financial ecosystem. Let's explore the key components that make up decentralized Finance.
- Blockchain Technology: DeFi relies on blockchain technology, specifically public blockchains like Ethereum, which provide a secure and transparent ledger for recording transactions. The blockchain acts as a decentralized database, enabling the execution and validation of smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with predefined rules.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts play a crucial role in DeFi. They are programmable contracts that automatically execute predefined actions when specific conditions are met. In DeFi, smart contracts facilitate various financial operations such as lending, borrowing, trading, and more. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): DeFi DApps are applications built on blockchain networks that offer financial services to users. These applications typically interact with smart contracts to facilitate transactions and provide users with functionalities such as lending platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming, stablecoins, insurance, etc.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs are a fundamental component of DeFi, enabling peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without the need for intermediaries. DEXs operate through smart contracts, allowing users to trade directly from their wallets. Liquidity pools, automated market makers (AMMs), and other mechanisms ensure the availability of trading pairs and efficient price discovery.
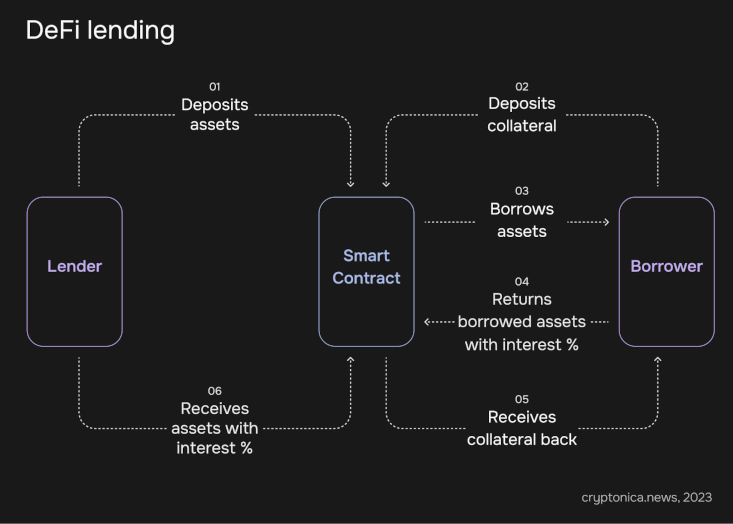
- Lending and Borrowing Platforms: DeFi lending and borrowing platforms enable individuals to lend their cryptocurrencies and earn interest or borrow assets by leveraging their existing holdings as collateral. These platforms match lenders and borrowers through smart contracts and often utilize algorithms to determine interest rates.
- Governance Tokens: Many DeFi protocols employ governance tokens that give holders the right to participate in decision-making processes concerning the protocol's future development and governance. These tokens often grant voting rights and incentivize token holders to actively engage in the platform.
- Decentralized Oracles: DeFi applications often require real-world data to execute smart contracts accurately. Decentralized oracles act as bridges between blockchain and external data sources, ensuring the transparency and reliability of information used in DeFi protocols.
- Interoperability and composability: DeFi is built on the principle of composability, which allows different DeFi protocols to interact and combine functionalities seamlessly. Interoperability enables users to utilize various DeFi services together, creating complex financial strategies and products.
These are some of the key components that make up decentralized Finance. DeFi is a rapidly evolving space, and new innovations and technologies continue to emerge, driving the growth and expansion of this transformative sector.

DeFi use cases
There is a wide range of use cases for DeFi, ranging from trading and lending to insurance and derivatives. Here are some of the most popular use cases:
- Trading: DeFi applications enable users to trade cryptocurrencies with minimal fees and without relying on centralized exchanges. DEXs provide liquidity pools that facilitate peer-to-peer trading while ensuring secure transactions.
- Lending: DeFi protocols allow users to lend and borrow digital assets with minimal risk. Automated smart contracts facilitate lending, enabling lenders to earn interest on their holdings while borrowers can access capital without involving intermediaries.
- Insurance: Decentralized insurance platforms provide users with an alternative to traditional insurance policies by leveraging smart contracts and blockchain technology. By pooling funds in a decentralized manner, these platforms make it easy for users to purchase insurance for their digital assets.
- Derivatives: DeFi derivatives enable users to speculate on the price movements of cryptocurrencies without actually holding them. These instruments use smart contracts to facilitate trading activities while providing investors with additional hedging opportunities.
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins are crypto assets designed to maintain a stable value by pegging them to other assets like fiat currencies or commodities. They provide stability within the volatile crypto market and are widely used in DeFi applications for trading, lending, and as a unit of account.
- Yield Farming: Yield farming is a type of liquidity mining that incentivizes users to provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges. By staking their funds in these liquidity pools, users can earn rewards in the form of tokens from the protocols they are participating in.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs are unique digital assets with cryptographic properties that cannot be replicated or interchanged. They are increasingly being used for art, gaming, and trading of unique digital items, with DeFi protocols providing secondary markets to facilitate the exchange of these assets.
Here are some of the most popular use cases for DeFi. As the sector continues to expand, we can expect to see even more creative and innovative use cases in the future.
Centralized Finance vs. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Centralized Finance (CeFi) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) are two distinct financial ecosystems that have emerged in recent years.
Centralized Finance
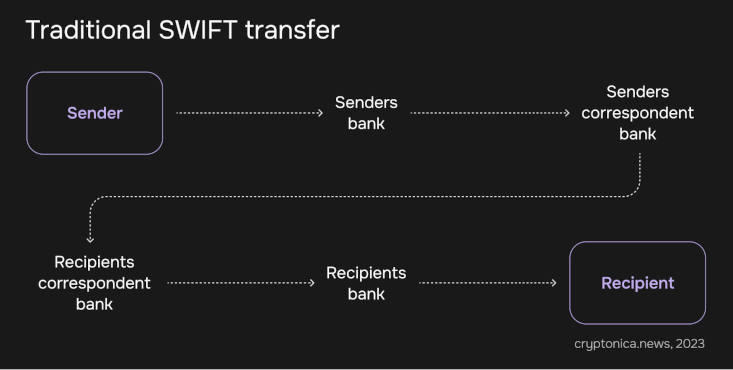
Centralized Finance (CeFi) refers to traditional financial systems and institutions where intermediaries like banks, governments, and other centralized entities control and manage financial transactions. In CeFi, individuals rely on these intermediaries to access and control their funds, and transactions are subject to regulations and oversight. In addition, CeFi is typically used for more traditional banking services such as deposits, loans, and payments.
Decentralized Finance
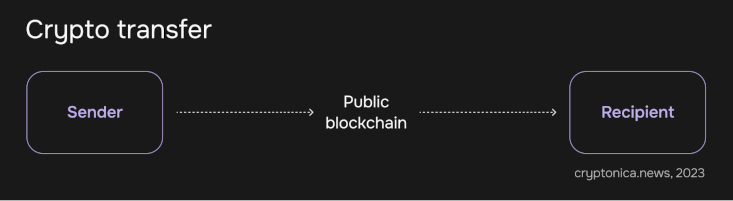
On the other hand, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a financial system built on blockchain technology that aims to eliminate intermediaries and enable peer-to-peer transactions. DeFi operates through smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements that automatically execute transactions when certain conditions are met. DeFi platforms provide various financial services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and more, without relying on centralized authorities.
Comparison: DeFi Vs. CeFi
- Control and Ownership: In CeFi, individuals entrust their funds to centralized entities, such as banks, which have control over their assets. In DeFi, individuals have complete control and ownership of their funds as they interact directly with smart contracts, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
- Accessibility: CeFi typically requires individuals to meet certain eligibility criteria and comply with regulatory requirements, making financial services accessible to a limited portion of the population. DeFi, being decentralized, allows anyone with an internet connection to access financial services, promoting financial inclusion.
- Intermediaries and Trust: CeFi relies on intermediaries to facilitate transactions and maintain trust. However, these intermediaries can be vulnerable to hacks, mismanagement, or censorship. DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries, relying on transparent and auditable smart contracts, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Transparency and Security: CeFi often lacks transparency, as individuals have limited visibility into the inner workings of financial institutions. DeFi, built on blockchain technology, offers transparent and immutable transaction records that anyone can audit. Moreover, DeFi platforms implement various security measures to protect user assets.
- Innovation and Flexibility: CeFi systems are generally slower to adopt new technologies and innovations due to the involvement of centralized decision-making processes. DeFi, being a permissionless and open ecosystem, fosters rapid innovation, allowing developers to build new decentralized applications (dApps) and experiment with novel financial products.
Note: As per the above comparison, both CeFi and DeFi have their merits and cater to different needs, and the choice between them depends on an individual's preferences, risk tolerance, and the specific use case at hand.
Key Benefits of DeFi
DeFi has many benefits over traditional Finance, including:
- Accessibility: DeFi provides financial services to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location or financial status. This is particularly useful for individuals in countries with limited access to banking services.
- Lower Costs and Faster Transactions: By eliminating the need for intermediaries, DeFi reduces the cost of financial transactions and significantly speeds up the process.
- Security: By relying on cryptographic tools like smart contracts, DeFi ensures that user funds are safe and secure from unauthorized access or manipulation.
- Decentralization: Since DeFi operates without a centralized intermediary, there is no single point of failure or censorship.
- Automation: DeFi transactions are automated through smart contracts, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Transparency: All DeFi transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain, ensuring participant transparency and accountability.
- Flexibility: DeFi allows users to customize their financial services according to their needs and preferences by eliminating intermediaries.
These are just a few of the many benefits offered by DeFi, and as the sector continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative use cases and benefits emerge.

Risks of DeFi for investors
Although DeFi offers many benefits, a few potential risks are associated with investing in DeFi projects. These include:
- Regulatory risk: Since DeFi is still relatively new and unregulated, there is a risk that regulations may change or be implemented in the future that could adversely affect investors and projects involved in DeFi.
- Security risk: DeFi projects are susceptible to hacks, as they often lack the security measures of traditional financial systems. As such, investors should be aware of the risks associated with investing in unsecured DeFi platforms.
- Liquidity risk: Many DeFi tokens and projects have limited liquidity, which can make it difficult for investors to exit a position without incurring large losses.
- Volatility risk: Many DeFi tokens are highly volatile, meaning their prices can swing drastically in a short period of time. This type of volatility makes investing in DeFi risky, as there is no guarantee that an investment will remain profitable over the long term.
While DeFi offers many benefits over traditional Finance, it also has its own set of risks. As such, investors should do their due diligence and weigh the pros and cons before investing in DeFi projects.
The Future of DeFi
The future of DeFi looks very promising, as the sector is expected to continue its rapid growth in the coming years. More and more projects are being built on top of decentralized networks, and it is likely that we will see more innovative use cases emerge in the near future.
DeFi could also play an important role in driving financial inclusion, as it offers financial services to anyone with an internet connection, no matter their location or financial status. Moreover, DeFi projects are also creating new investment opportunities that could provide investors with access to a broader range of assets and generate higher returns than traditional investments.
As more people become aware of the potential offered by DeFi, we can expect to see increased adoption in the coming years. Therefore, now is a great time to learn about DeFi and get involved in the sector.
The increasing popularity of DeFi will also lead to more regulation from governments across the world, which could reinforce trust and confidence in the sector. With increasing regulatory clarity, we can expect even more people to join the DeFi revolution and reap its many rewards.

Conclusion
To conclude, DeFi is a new form of digital Finance that offers numerous benefits over traditional financial systems. It is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, is secure and transparent, and allows users to customize their financial services according to their needs. Moreover, the sector is rapidly evolving, creating more investment opportunities for investors looking for higher returns.
Although investing in DeFi comes with its own set of risks, these can be mitigated by doing due diligence and understanding the potential rewards and risks associated with investing in DeFi projects. As such, now is a great time to learn about DeFi and get involved in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bitcoin a Decentralized Finance?
No, Bitcoin is not a Decentralized Finance, but it is an essential part of the DeFi ecosystem as it acts as a medium for digital transactions. Moreover, numerous DeFi projects are built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain or use its native token, BTC. Therefore, while Bitcoin isn't a Decentralized Finance, it is an important part of the DeFi space.
How do I make money with DeFi?
There are several ways to make money with DeFi, such as providing liquidity to projects through liquidity pools, lending and borrowing digital assets on DeFi platforms, staking cryptocurrencies for rewards, or investing in tokens associated with new projects.
Is investing in DeFi safe?
Investing in DeFi comes with its own set of risks, and it is important to do due diligence and understand the potential rewards and risks associated with investing in DeFi projects. However, if done correctly, investing in DeFi can be lucrative and offers higher returns than traditional investments.
When will DeFi go mainstream?
While it is difficult to predict when exactly DeFi will go mainstream, its increasing popularity and adoption suggest that its widespread use is just around the corner. As more people become aware of the benefits of DeFi, we can expect to see increased adoption in the coming years. Moreover, increasing regulatory clarity could also be instrumental in driving mainstream acceptance of DeFi projects. Thus, it is safe to assume that DeFi will go mainstream in the near future.






























